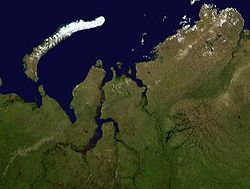
Gyda Peninsula
The Gyda Peninsula (Russian: Гыда́нский полуо́стров, romanized: Gydansky poluostrov) is a geographical feature of the Siberian coast in the Kara Sea.
A notable archeological find from the peninsula is a mammoth skeleton, now housed in a zoological museum in Saint Petersburg.
[7] In 2016, after a hiatus of 25 years (the local research station was closed in 1991), scientists were allowed back on the site to lead geo-cryological studies and monitor the permafrost.
[8] In 2020, officially following the warmest summer recorded in the region since 1881, heavy masses of mud and permafrost started to slide into the sea of the Gydan Bay.
[9] The mudslides have also been attributed to the recent launch of the Arctic LNG 2 project, an enormous natural gas extraction site built in the region.