High-performance liquid chromatography
Its composition and temperature play a major role in the separation process by influencing the interactions taking place between sample components and adsorbent.
This gives HPLC superior resolving power (the ability to distinguish between compounds) when separating mixtures, which makes it a popular chromatographic technique.
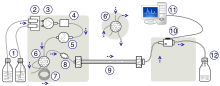
[citation needed] The schematic of an HPLC instrument typically includes solvents' reservoirs, one or more pumps, a solvent-degasser, a sampler, a column, and a detector.
Some models of mechanical pumps in an HPLC instrument can mix multiple solvents together at a ratios changing in time, generating a composition gradient in the mobile phase.
[citation needed] The sample mixture to be separated and analyzed is introduced, in a discrete small volume (typically microliters), into the stream of mobile phase percolating through the column.
[22] Gas amplifier pumps were ideal because they operated at constant pressure and did not require leak-free seals or check valves for steady flow and good quantitation.
[18] Hardware milestones were made at Dupont IPD (Industrial Polymers Division) such as a low-dwell-volume gradient device being utilized as well as replacing the septum injector with a loop injection valve.
The practical disadvantages stem from the excessive pressure drop needed to force mobile fluid through the column and the difficulty of preparing a uniform packing of extremely fine materials.
The 1952 Nobel Prize in chemistry was earned by Archer John Porter Martin and Richard Laurence Millington Synge for their development of the technique, which was used for their separation of amino acids.
[citation needed] Partition- and NP-HPLC fell out of favor in the 1970s with the development of reversed-phase HPLC because of poor reproducibility of retention times due to the presence of a water or protic organic solvent layer on the surface of the silica or alumina chromatographic media.
[citation needed] Recently, partition chromatography has become popular again with the development of Hilic bonded phases which demonstrate improved reproducibility, and due to a better understanding of the range of usefulness of the technique.
Most of the current methods of separation of biomedical materials use C-18 type of columns, sometimes called by a trade names such as ODS (octadecylsilane) or RP-18 (Reversed Phase 18).
[citation needed] RP-HPLC operates on the principle of hydrophobic interactions, which originates from the high symmetry in the dipolar water structure and plays the most important role in all processes in life science.
In theory, an analyte with a larger hydrophobic surface area (C–H, C–C, and generally non-polar atomic bonds, such as S-S and others) can be retained longer as it does not interact with the water structure.
They are rarely used in mass spectrometry methods, due to residues it can leave in the detector and solvent delivery system, which interfere with the analysis and detection.
There are selected brands of hybrid or enforced silica based particles of RP columns which can be used at extreme pH conditions.
The use of extreme acidic conditions is also not recommended, as they also might hydrolyzed as well as corrode the inside walls of the metallic parts of the HPLC equipment.
[citation needed].. Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC)[30] separates polymer molecules and biomolecules based on differences in their molecular size (actually by a particle's Stokes radius).
On the other hand, the bigger the molecular size, the higher the probability the molecule will not fully penetrate the pores of the stationary phase, and even travel around them, thus, will be eluted earlier.
Small molecules will permeate fully through the pores of the stationary phase particles and will be eluted last, marking the end of the chromatogram, and may appear as a total penetration marker.
Cellulose and dextran ion exchangers possess larger pore sizes and low charge densities making them suitable for protein separation.
High performance affinity chromatography (HPAC)[33] works by passing a sample solution through a column packed with a stationary phase that contains an immobilized biologically active ligand.
Using a weaker mobile phase, the runtime is lengthened and results in slowly eluting peaks to be broad, leading to reduced sensitivity.
In gradient conditions, where the mobile phase changes with time during the chromatographic run, it is more appropriate to use the parameter peak capacity Pc as a measure for the system efficiency.
It can also affect the separation selectivity, when flow rate and injection volumes are not scaled down or up proportionally to the smaller or larger diameter used, both in the isocratic and in gradient modes.
Pumps vary in pressure capacity, but their performance is measured on their ability to yield a consistent and reproducible volumetric flow rate.
When used with an electrochemical detector (ECD) the HPLC-ECD selectively detects neurotransmitters such as: norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, glutamate, GABA, acetylcholine and others in neurochemical analysis research applications.
Similar assays can be performed for research purposes, detecting concentrations of potential clinical candidates like anti-fungal and asthma drugs.
[79] While urine is the most common medium for analyzing drug concentrations, blood serum is the sample collected for most medical analyses with HPLC.
[82][83] The infants' samples come in the shape of dried blood spot (DBS),[84] which is simple to prepare and transport, enabling safe and accessible diagnostics, both locally and globally.