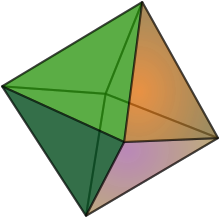
Hexany
In musical tuning systems, the hexany, invented by Erv Wilson,[1] represents one of the simplest structures found in his combination product sets.
The Euler Fokker Genus fails to see 1 as a possible member of a set except as a starting point.
hexany is the name that Erv Wilson gave to the six notes in the 2-out-of-4 combination product set, abbreviated as 2*4 CPS.
The possibility of an octave being a solution is not outside of Wilson's conception and is used in cases of placing larger combination product sets upon Generalized Keyboards.
For example, the face with vertices 3×5, 1×5, 5×7 is an otonal (major type) chord since it can be written as 5×(1, 3, 7), using low numbered harmonics.
Composers including Kraig Grady, Daniel James Wolf, and Joseph Pehrson have used pitch structures based on hexanies.