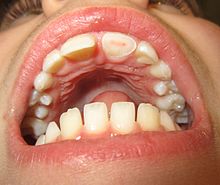
Human tooth
Human teeth function to mechanically break down items of food by cutting and crushing them in preparation for swallowing and digesting.
Primary teeth typically start to appear ("erupt") around six months of age and this may be distracting and/or painful for the infant.
This information serves a practical purpose for dentists, enabling them to easily identify and describe teeth and structures during treatment.
Enamel varies in thickness over the surface of the tooth and is often thickest at the cusp, up to 2.5mm, and thinnest at its border, which is seen clinically as the CEJ.
[16] Because it is softer than enamel, it decays more rapidly and is subject to severe cavities if not properly treated, but dentin still acts as a protective layer and supports the crown of the tooth.
Tooth development is the complex process by which teeth form from embryonic cells, grow, and erupt into the mouth.
Another, known as the cushioned hammock theory, resulted from microscopic study of teeth, which was thought to show a ligament around the root.
The onset of primary tooth loss has been found to correlate strongly with somatic and psychological criteria of school readiness.
Alveolar bone surrounds the roots of teeth to provide support and creates what is commonly called an alveolus, or "socket".
The microorganisms that form the biofilm are almost entirely bacteria (mainly streptococcus and anaerobes), with the composition varying by location in the mouth.
Dental caries (cavities), described as "tooth decay", is an infectious disease which damages the structures of teeth.
Dental caries has a long history, with evidence showing the disease was present in the Bronze, Iron, and Middle ages but also prior to the neolithic period.
[49][50] The resulting acidic levels in the mouth affect teeth because a tooth's special mineral content causes it to be sensitive to low pH.
Regular cleanings, usually done by dentists and dental hygienists, remove tartar (mineralized plaque) that may develop even with careful brushing and flossing.
Professional cleaning includes tooth scaling, using various instruments or devices to loosen and remove deposits from teeth.
[52] Healthcare professionals recommend regular brushing twice a day (in the morning and in the evening, or after meals) in order to prevent formation of plaque and tartar.
When used correctly, dental floss removes plaque from between teeth and at the gum line, where periodontal disease often begins and could develop caries.
"[53] The most important advantage of electric toothbrushes is their ability to aid people with dexterity difficulties, such as those associated with rheumatoid arthritis.
Sealants can last up to ten years and are primarily used on the biting surfaces of molars of children and young adults, especially those who may have difficulty brushing and flossing effectively.
Sealants are applied in a dentist's office, sometimes by a dental hygienist, in a procedure similar in technique and cost to a fluoride application.
Restorations may be created from a variety of materials, including glass ionomer, amalgam, gold, porcelain, and composite.
Demarcated opacities of enamel have sharp boundaries where the translucency decreases and manifest a white, cream, yellow, or brown color.
[60] Dental fluorosis is a condition which results from ingesting excessive amounts of fluoride and leads to teeth which are spotted, yellow, brown, black or sometimes pitted.
[68] Signs of tooth destruction from erosion is a common characteristic in the mouths of people with bulimia since vomiting results in exposure of the teeth to gastric acids.
Discoloration of teeth may result from bacteria stains, tobacco, tea, coffee, foods with an abundance of chlorophyll, restorative materials, and medications.
Amalgam, a common dental restorative material, may turn adjacent areas of teeth black or gray.
Erythroblastosis fetalis and biliary atresia are diseases which may cause teeth to appear green from the deposition of biliverdin.
[75] This is important to consider in order to correctly plan treatment keeping in mind considerations for function and aesthetics.
There have been a plethora of research studies to calculate prevalence of certain dental anomalies in CLP populations however a variety of results have been obtained.
It is essential to assess the patient both clinically and radiographically in order to correctly treat and prevent progression of any dental problems.




A: tooth
B: gingiva
C: bone
D: periodontal ligaments