Iron pillar of Delhi
The pillar weighs more than six tonnes and is thought to have been erected elsewhere, possibly outside the Udayagiri Caves,[3] and moved to its present location by Anangpal Tomar in the 11th century.
The oldest inscription on the pillar is that of a king named Chandra (IAST: Candra), generally identified as the Gupta emperor Chandragupta II.
[12] The text has some unusual deviations from the standard Sanskrit spelling, such as:[11] In 1831, the East India Company officer William Elliott made a facsimile of the inscription.
Based on this copy, Bhau Daji Lad published a revised text and translation in 1875, in Journal of the Bombay Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society.
[11] Following is the Roman script transliteration of the text:[24] Yasy odvarttayah-pratīpamurasā śattrun sametyāgatan Vańgeshvāhava varttinosbhilikhitā khadgena kīrttir bhuje Tirtvā sapta mukhāni yena samare sindhor jjitā Vāhlikāyasyādya pyadhivāsyate jalanidhir vviryyānilair ddakshinah Khinnasy eva visrijya gām narapater ggāmāśritasyaetrām mūr(t)yā karmma-jitāvanim gatavatah kīrt(t)yā sthitasyakshitau Śāntasyeva mahāvane hutabhujo yasya pratāpo mahānnadhayā pyutsrijati pranāśista-ripor Yyatnasya śesahkshitim Prāptena sva bhuj ārjitan cha suchiran ch aikādhirājayam kshitau chandrāhvena samagra chandra sadriśīm vaktra-śriyam bibhratā Tenāyam pranidhāya bhūmipatinā bhāveva vishno (shnau) matim prānśurvisnupade girau bhagavato Vishnuordhidhvajah sthāpitah J. F. Fleet's 1888 translation is as follows:[25] (Verse 1) He, on whose arm fame was inscribed by the sword, when, in battle in the Vanga countries (Bengal), he kneaded (and turned) back with (his) breast the enemies who, uniting together, came against (him); – he, by whom, having crossed in warfare the seven mouths of the (river) Sindhu, the Vahlikas were conquered; – he, by the breezes of whose prowess the southern ocean is even still perfumed; – (Verse 2) He, the remnant of the great zeal of whose energy, which utterly destroyed (his) enemies, like (the remnant of the great glowing heat) of a burned-out fire in a great forest, even now leaves not the earth; though he, the king, as if wearied, has quit this earth, and has gone to the other world, moving in (bodily) form to the land (of paradise) won by (the merit of his) actions, (but) remaining on (this) earth by (the memory of his) fame; – (Verse 3) By him, the king, attained sole supreme sovereignty in the world, acquired by his own arm and (enjoyed) for a very long time; (and) who, having the name of Chandra, carried a beauty of countenance like (the beauty of) the full-moon,-having in faith fixed his mind upon (the god) Vishnu, this lofty standard of the divine Vishnu was set up on the hill (called) Vishnupada.
The inscription has been revisited by Michael Willis in his book Archaeology of Hindu Ritual, his special concern being the nature of the king's spiritual identity after death.
His reading and translation of verse 2 is as follows:[26] [khi]nnasyeva visṛjya gāṃ narapater ggām āśritasyetarāṃ mūrtyā karrmajitāvaniṃ gatavataḥ kīrtyā sthitasya kṣitau [*|] śāntasyeva mahāvane hutabhujo yasya pratāpo mahān nādyāpy utsṛjati praṇāśitaripor yyatnasya śeṣaḥ kṣitim [||*] The Sanskrit portion given above can be translated as follows:[26] The residue of the king's effort – a burning splendour which utterly destroyed his enemies – leaves not the earth even now, just like (the residual heat of) a burned-out conflagration in a great forest.
[27] The king's conquest of heaven combined with the description of him resorting to the other world in bodily form (gām āśritasyetarāṃ mūrtyā), confirms our understanding of the worthy dead as autonomous theomorphic entities.
J. F. Fleet (1898) identified this place with Mathura, because of its proximity to Delhi (the find spot of the inscription) and the city's reputation as a Vaishnavite pilgrimage centre.
[35] The key point in favour of placing the iron pillar at Udayagiri is that this site was closely associated with Chandragupta and the worship of Vishnu in the Gupta period.
[28] Pasanaha Chariu, an 1132 CE Jain Apabhramsha text composed by Vibudh Shridhar, states that "the weight of his pillar caused the Lord of the Snakes to tremble".
In a report published in the journal Current Science, R. Balasubramaniam of IIT Kanpur explains how the pillar's resistance to corrosion is due to a passive protective film at the iron-rust interface.
The next main agent to intervene in protection from oxidation is phosphorus, enhanced at the metal–scale interface by the same chemical interaction previously described between the slags and the metal.
The use of limestone as in modern blast furnaces yields pig iron that is later converted into steel; in the process, most phosphorus is carried away by the slag.
This high phosphorus content and particular repartition are essential catalysts in the formation of a passive protective film of misawite (d-FeOOH), an amorphous iron oxyhydroxide that forms a barrier by adhering next to the interface between metal and rust.
Misawite, the initial corrosion-resistance agent, was thus named because of the pioneering studies of Misawa and co-workers on the effects of phosphorus and copper and those of alternating atmospheric conditions in rust formation.
[42] The most critical corrosion-resistance agent is iron hydrogen phosphate hydrate (FePO4-H3PO4-4H2O) under its crystalline form and building up as a thin layer next to the interface between metal and rust.
[40] In 1969, in his first book, Chariots of the Gods?, Erich von Däniken cited the absence of corrosion on the Delhi pillar and the unknown nature of its creation as evidence of extraterrestrial visitation.
[43][44] When informed by an interviewer, in 1974, that the column was not in fact rust-free, and that its method of construction was well-understood, von Däniken responded that he no longer considered the pillar or its creation to be a mystery.
[50] A significant indentation on the middle section of the pillar, approximately 4 m (13 ft) from the current courtyard ground level, has been shown to be the result of a cannonball fired at close range.
While no contemporaneous records, inscriptions, or documents describing the event are known to exist, historians generally agree that Nadir Shah is likely to have ordered the pillar's destruction during his invasion of Delhi in 1739, as he would have considered a Hindu temple monument undesirable within an Islamic mosque complex.




 ) on the iron pillar of Delhi, thought to represent
Chandragupta II
.
Gupta script
: letter "Ca"
) on the iron pillar of Delhi, thought to represent
Chandragupta II
.
Gupta script
: letter "Ca"
 , followed by the
conjunct consonant
"ndra" formed of the vertical combination of the three letters
n
, followed by the
conjunct consonant
"ndra" formed of the vertical combination of the three letters
n
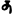 d
d
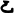 and
r
and
r
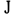 .
[
17
]
[
18
]
.
[
17
]
[
18
]



