James S. Albus
[2] From 1957 to 1973 Albus worked at NASA starting in 1957 as Physicist-Engineer on Project Vanguard at the Naval Research Laboratory, Washington DC.
Here he founded the Robot Systems Division, developed the RoboCrane, and many applications of the RCS architecture for DARPA, NASA, ARL, U.S. Bureau of Mines, Ford, and General Motors.
He developed the 4D/RCS architecture for the Army Research Lab (ARL) Demo III Experimental Unmanned Vehicle program.
[2] In 1962 he received the highest NASA cash award granted to that time for the invention of the Digital Solar Aspect Sensor.
[2] Albus made contributions to cerebellar robotics, developed a two-handed manipulator system known as the Robocrane (a crane-like variation on the Stewart platform idea), and proposed an economic concept known as "Peoples' Capitalism".
[4] Albus invented and developed a new generation of robot cranes based on six cables and six winches configured as a Stewart platform.
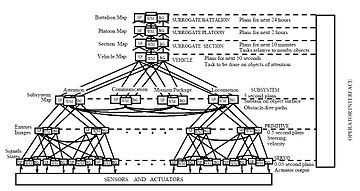
for a number of intelligent systems including the NBS Automated Manufacturing Research Facility (AMRF), the NASA telerobotic servicer, a DARPA Multiple Autonomous Undersea Vehicle project, a nuclear Submarine Operational Automation System, a Post Office General Mail facility, a Bureau of Mines automated mining system, a commercial open architecture machine tool controller, and numerous advanced robotic projects, including the Army Research Lab Demo III Experimental Unmanned Ground vehicle.
RCS - for Real-time Control System) provided the fundamental integrating principle of the National Bureau of Standards (NBS) Automated Manufacturing Research Facility (AMRF.)