Military history of Japan
[10] The pottery style characteristic of the first phases of Jōmon culture was decorated by impressing cords into the surface of wet clay and is generally accepted to be among the oldest in East Asia and the world.
The transition from the Jōmon to Yayoi, and later to the Yamato period, is likely to have been characterized by violent struggle as the natives were displaced and assimilated by the invaders with their vastly superior military technology.
[21] The Heian Period marks a crucial shift, away from a state that was united in relative peace against outside threats to one that did not fear invasion and, instead, focused on internal division and clashes between ruling factions of samurai clans, over political power and control of the line of succession to the Chrysanthemum Throne.
They did not select individual opponents with whom to conduct honorable duels, but rode forth on horseback, with various forms of gunpowder weapons and the famous Mongol bow, charging into enemy lines and killing as many as they could without regard to Japanese conceptions of protocol.
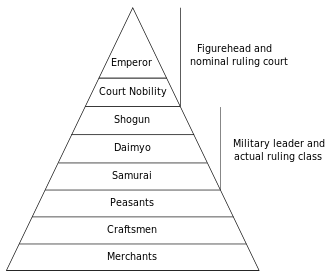
The authority of both the shogunate and the Imperial Court had weakened, and provincial Governors (shugo) and other local samurai leaders emerged as the daimyōs, who battled each other, religious factions (e.g. the Ikkō-ikki), and others for land and power for the next 150 years or so.
Over one hundred domains clashed and warred throughout the archipelago, as clans rose and fell, boundaries shifted, and some of the largest battles in all of global pre-modern history were fought.
The composition of the army changed, with masses of ashigaru, footsoldiers armed with long lances (yari), archers, and, later, gunners serving alongside mounted samurai.
It's named for the increasingly important castle-cities, is marked by the introduction of firearms, after contact with the Portuguese, and a further push towards all-out battle, away from individual combats and concepts of personal honor and bravery.
The 1575 Battle of Nagashino, in which about 3,000 arquebusiers led by Oda Nobunaga cut down charging ranks of thousands of samurai, remains one of the chief examples of the effect of these weapons.
Though civil strife continued to rage as it had for the previous century, the battles growing larger and more tactically complex, it was at this time that the many "warring states" began to be united.
[47] The Japanese army quickly captured several major cities from the unprepared Joseon kingdom including the capital, causing the king to retreat and request military aid from China.
Concurrently, the "Righteous Army" of Korean civilians waged guerilla warfare and Admiral Yi Sun-sin repeatedly disrupted the Japanese supply lines at sea.
Though the actual end of the shogunate and establishment of an Imperial Western-style government was handled peacefully, through political petitions and other methods, the years surrounding the event were not entirely bloodless.
The Japanese people and the government with Emperor Meiji realized that in order to preserve the independence of Japan it had to modernize to become an equal of the western colonial powers.
[63] In 1873, the Imperial government asked the newly appointed War Minister Yamagata Aritomo (山縣 有朋, June 14, 1838 – February 1, 1922) to organize a national army for Japan.
[66] Captain Jules Brunet, initially a French artillery advisor of the Japanese central government, eventually took up arms alongside the Shōgun Tokugawa Yoshinobu's army against the Imperial troops during the Boshin War.
The war demonstrated the failure of the Qing dynasty's attempts to modernize its military and fend off threats to its sovereignty, especially when compared with Japan's successful Meiji Restoration.
Following the First Sino-Japanese War (1894–1895), and the humiliation of the forced return of the Liaotung peninsula to China under Russian pressure (the "Triple Intervention"), Japan began to build up its military strength in preparation for further confrontations.
Japan promulgated a ten-year naval build-up program, under the slogan "Perseverance and determination" (Jp:臥薪嘗胆, Gashinshoutan), in which it commissioned 109 warships, for a total of 200,000 tons, and increased its Navy personnel from 15,100 to 40,800.
Japanese military superiority over a weak and demoralized Chinese Republican army allowed for swift advances down the eastern coast, leading to the fall of Shanghai and Nanjing (the then capital of the Republic of China) the same year.
In July 1940, the U.S. banned the shipment of aviation gasoline to Japan, while Imperial Japanese Army invaded French Indochina and occupied its naval and air bases in September 1940.
Following Japan's refusal to withdraw from the Republic of China (with the exclusion of Manchukuo) and Indochina; the United States, Great Britain, and the Netherlands imposed an embargo (22 July 1941) on gasoline, while shipments of scrap metal, steel, and other materials had virtually ceased.
Fred Borch explained: As Japan continued its modernization in the early 20th century, her armed forces became convinced that success in battle would be assured if Japanese soldiers, sailors, and airmen had the "spirit" of Bushido.
Consequently, when the Japanese murdered POWs by shooting, beheading, and drowning, these acts were excused since they involved the killing of men who had forfeited all rights to be treated with dignity or respect.
The last sentence is indicative: it is according to the dictates of time and fate that We have resolved to pave the way for a grand peace for all the generations to come by enduring the unendurable and suffering what is unsufferable.
Japan has increased its power projection capabilities such as with the development of homemade long-range cruise missiles, the Amphibious Rapid Deployment Brigade and the modification of two Izumo-class destroyers into de facto aircraft carriers with F-35Bs.
[154] Since March 2016, Japan's Legislation for Peace and Security enables seamless responses of the JSDF to any situation to protect the lives and livelihood of Japanese people.
China built military outposts on islands which intimidate and violate the territorial claims of other countries like Taiwan, Vietnam, Malaysia, Indonesia, Brunei and the Philippines.
50 ARDB soldiers were deployed with 4 armored vehicles for the first time in an overseas training exercise with American and Filipino marines in Operation Kamandag in Luzon, the Philippines from 2 to 11 October 2018.
[176] On May 28, 2019, President of the United States Donald Trump inspected the JS Kaga, the second ship in the Izumo class, during his visit in Japan and supported the country's effort for an active role in the defense and security of the Pacific region.