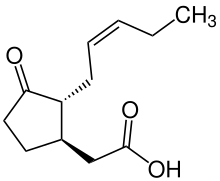
Jasmonic acid
Jasmonic acid (JA) is an organic compound found in several plants including jasmine.
It was first isolated in 1957 as the methyl ester of jasmonic acid by the Swiss chemist Édouard Demole and his colleagues.
The Dgl gene is responsible for maintaining levels of JA during usual conditions in Zea mays as well as the preliminary release of jasmonic acid shortly after being fed upon.
[4] When plants are attacked by insects, they respond by releasing JA, which activates the expression of protease inhibitors, among many other anti-herbivore defense compounds.
[10] This production of protease inhibitor can protect the plant from insects, decreasing infestation rates and physical damage sustained due to herbivores.
[12] In Zea mays, salicylic acid and JA are mediated by NPR1 (nonexpressor of pathogenesis-related genes1), which is essential in preventing herbivores from exploiting this antagonistic system.