Bernese Jura Railway
The Central Railway's construction now concentrated for a period on the more populated areas in the Swiss Plateau.
The municipalities and Bürgergemeinden of the Jura purchased a total of over 7 million shares, partially exploiting their forests to fund them.
The Jura bernois began construction and opened individual sections of its network between Biel, Convers (near La Chaux-de-Fonds), Delle and Basel between 1872 and 30 March 1877.
It took over the Bernese State Railway (Bernische Staatsbahn, BSB), including the Zollikofen–Biel –La Neuveville line in 1877.
The canton of Bern received JB shares worth CHF 11.56 million in return.
[note 3] Ten years after its construction, the Canton of Neuchâtel exercised its buyback right and acquired the Neuchâtel–La Chaux-de-Fonds–Le Locle line on 1 January 1886 for around CHF 5 million,[note 4] so it could lease it to the newly established Jura neuchâtelois (JN).
With the opening of the first, over 44 km long section from Alpnachstad via the Brünig Pass to Brienz on 14 June 1888, the network of the JBL was significantly extended.
The metre-gauge line with sections of rack connects the two tourist regions of Central Switzerland and the Bernese Highlands.
Only the JS had sufficient resources to progress on the construction of the Simplon Tunnel that had been planned for decades.
The bridge over the Birs built by Gustave Eiffel for the Bernese Jura collapsed shortly after the merger.





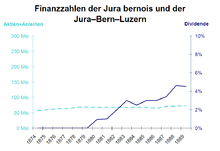
The positive operating results allowed the Jura–Bern–Luzern , to pay a dividend every year.



