Kingdom of Bavaria
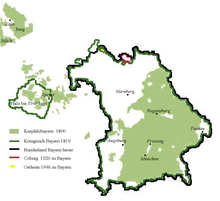
[4] The polity's foundation dates back to the ascension of Elector Maximilian IV Joseph of the House of Wittelsbach as King of Bavaria in 1806.
Charles Theodore, who had done nothing to prevent the war or to resist the invasion, fled to Saxony, leaving a regency, the members of which signed a convention with Moreau, by which he granted an armistice in return for a heavy contribution (7 September 1796).
With the Treaty of Ried of 8 October 1813 Bavaria left the Confederation of the Rhine and agreed to join the Sixth Coalition against Napoleon in exchange for a guarantee of her continued sovereign and independent status.
Between 1799 and 1817, the leading minister Count Montgelas followed a strict policy of modernisation and laid the foundations of administrative structures that survived even the monarchy and are (in their core) valid until today.
The monarchy appealed to Prussia and the Austria for advice; the two refused to take action on Bavaria's behalf, but the disturbances lessened and the state stabilized with the accession of Ludwig I to the throne following the death of Maximilian in 1825.
Within the Kingdom of Bavaria, the Palatinate enjoyed a special legal and administrative position, as the Bavarian government maintained substantial achievements of the French period.
In 1837, the Roman Catholic-supported clerical movement, the Ultramontanes, came to power in the Bavarian parliament and began a campaign of reform to the constitution, which removed civil rights that had earlier been granted to Protestants, as well as enforcing censorship and forbidding the free discussion of internal politics.
The revolutions also brought amendments to the constitution, including changes to the lower house of the Landtag with equal suffrage for every male who paid a direct tax.
However, when Maximilian II rejected the Frankfurt Constitution in 1849, there was an uprising in the Bavarian Palatinate under Joseph Martin Reichard, which was put down with the support of Prussian forces.
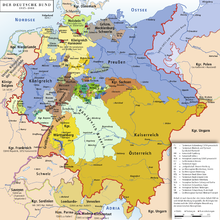
In the aftermath of the failure of the Frankfurt Parliament, Prussia and Austria continued to debate over which monarchy had the inherent right to rule Germany.
When the project to unite the German middle-sized powers under Bavarian leadership against Prussia and Austria (the so-called Trias) failed, Minister-President von der Pfordten resigned in 1859.
Prussia quickly defeated the Kingdom of Hanover, then won the Battle of Königgrätz (3 July 1866) against Austria, which sued for peace shortly afterward.
Bavaria's previous inhibitions towards Prussia changed, along with those of many of the south German states, after French Emperor Napoleon III began speaking of France's need for "compensation" from its loss in 1814 and included the Bavarian-held Palatinate as part of its territorial claims.
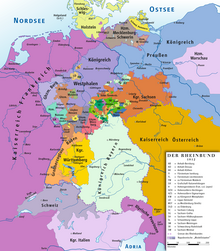
The Bavarian delegation under Count Otto von Bray-Steinburg had secured a privileged status for the Kingdom of Bavaria within the German Empire (Reservatrechte).
These debts caused much concern among Bavaria's political elite, who sought to persuade Ludwig to cease his building; he refused, and relations between the government's ministers and the crown deteriorated.
The official autopsy listed cause of death as suicide by drowning, but some sources claim that no water was found in Ludwig's lungs.
With the Centre politician Georg von Hertling the Prince Regent appointed a government headed by a representative of the Landtag's majority for the first time in 1912.
The Prinzregentenzeit ("prince's regent's time"), as the regency of Luitpold is often called, was an era of the gradual transfer of Bavarian interests behind those of the German Empire.
Finally, the constitutional amendment of 1913 brought the determining break in the continuity of the king's rule in the opinion of historians, particularly as this change had been granted by the Landtag as a House of Representatives and meant therefore indirectly the first step toward full parliamentary government.
These prince regent's years were transfigured, finally—above all in the retrospect – to a golden age of Bavaria, even if one mourned the "fairy tale king" Ludwig II, which happens in a folkloric-nostalgic manner till this day.
With the establishment of the German Empire, a series of conventions brought the bulk of the various state military forces directly under the administration of the Prussian War Ministry.
[11] The Bavarian infantry and cavalry regiments retained their historic light blue and green uniforms, distinctive from the Prussian model adopted throughout most of the army.
The individual Bavarian soldier swore an oath of loyalty to King Ludwig, though in wartime this pledge of obedience was extended to Kaiser Wilhelm as supreme commander.
[12] In 1914, a clash of alliances occurred over Austria-Hungary's invasion of Serbia following the assassination of Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand by a Bosnian Serb militant.
Later Ludwig even claimed annexations for Bavaria (Alsace[citation needed] and the city of Antwerp in Belgium, to receive access to the sea).
Rupprecht, Crown Prince of Bavaria did not wish to use the occasion of the passing of his father to attempt to re-establish the monarchy by force, preferring to do so by legal means.
Cardinal Michael von Faulhaber, Archbishop of Munich, in his funeral speech, made a clear commitment to the monarchy while Rupprecht only declared that he had stepped into his birthright.
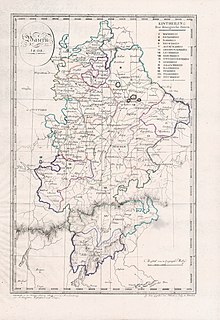
They were created in the fashion of the French departements, quite even in size and population, and named after their main rivers: Altmühl-, Eisack-, Etsch-, Iller-, Inn-, Isar-, Lech-, Main-, Naab-, Oberdonau-, Pegnitz-, Regen-, Rezat-, Salzach- and Unterdonaukreis.
Because of the numerous territorial changes in 1810 and 1815, the divisions needed to be adjusted and the number of Kreise was reduced to 8: Isar-, Unterdonau-, Oberdonau-, Regen-, Rezat-, Untermain-, Obermain- and Rheinkreis.
The electorate, a former dominion of the Bavarian Wittelsbach dynasty, had been split up in 1815, the eastern bank of the Rhine with the former capital Mannheim and Heidelberg was given to the Grand Duchy of Baden.