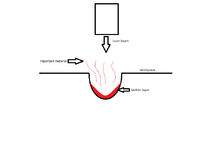
Laser beam machining
The high frequency of monochromatic light will fall on the surface, thus heating, melting and vaporizing the material due to the impinge of photons (see Coulomb explosion).
The synthetic ruby rod is optically pumped using a xenon flashtube before it is used as an active laser medium.
The material's reflectivity, density, specific heat, and melting point temperature all contribute to the lasers ability to cut the workpiece.
It is used in the automobile, shipbuilding, aerospace, steel, electronics, and medical industries for precision machining of complex parts.
Laser cladding is used to coat cheap or weak parts with a harder material in order to improve the surface quality.
In the electronic industry laser beam machining is used for wire stripping and skiving of circuits.