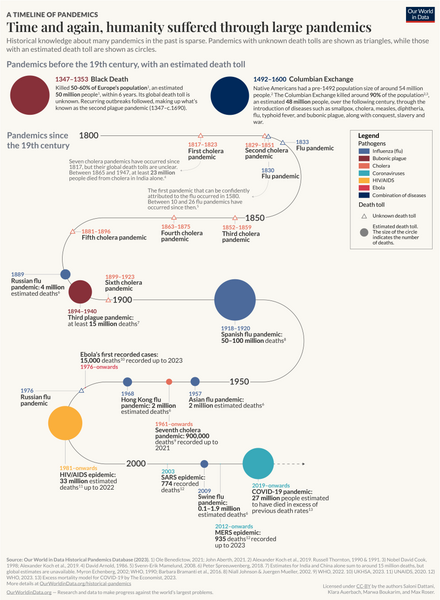
List of epidemics and pandemics
Infectious diseases with high prevalence are listed separately (sometimes in addition to their epidemics), such as malaria, which may have killed 50–60 billion people throughout history, or about half of all humans that have ever lived.
If the death toll averages of two or more epidemics or pandemics are equal, then the smaller the range, the higher the rank.
Western Hemisphere populations were ravaged mostly by smallpox, but also typhus, measles, influenza, bubonic plague, cholera, malaria, tuberculosis, mumps, yellow fever, and pertussis.
The lack of written records in many places and the destruction of many native societies by disease, war, and colonization make estimates uncertain.
There have been various major infectious diseases with high prevalence worldwide, but they are currently not listed in the above table as epidemics/pandemics due to the lack of definite data, such as time span and death toll.