List of sovereign states by date of formation
Cases like this occur when, for example, one state is annexed or conquered by another and ceases to exist even in nominal form (i.e., not even a "government in exile" is established).
1908-1960: Belgian Congo 1885-1908: Congo Free State 1879-1884: School War 1815-1830: Dutch Rule 1714-1793: Austrian Netherlands Belizean-Guatemalan territorial dispute 1783-1981: British Honduras Largely as a result of the costly military expeditions against the Maya, the expenses of administering the new colony of British Honduras increased, at a time when the economy was severely depressed.
After Antonio José de Sucre was elected as the second president, he convened the Constituent Assembly in Chuquisaca to determine the future of the region.
Almost all delegates wanted that Bolivia became an independent country and rejected any annexation to Argentina (former Río de la Plata) or Peru).
During the next decade, Diogo Gomes and António de Noli (also captains in the service of Prince Henry) discovered the remaining islands of the archipelago.
1945–1993: Part of the Czechoslovakia (interrupted by Warsaw Pact armies in 1968) 1945: Occupied by WWII Allies in 1945 1939–1945: Occupied by Germany 1918–1939: Part of the Czechoslovakia 1867–1918: Lands of the Bohemian Crown, held in personal union within Austria-Hungary 1806–1867: Lands of the Bohemian Crown, held in personal union within the Austrian Empire 1198–1806: Kingdom of Bohemia, State of the Holy Roman Empire (in personal union with Austria from 1526) 1002–1198: Duchy of Bohemia, State of the Holy Roman Empire 935–1002: Unified with Moravia and Silesia under Boleslaus I, Duke of Bohemia, who acceded to the throne in 935.
870–935: Duchy of Bohemia first independent from Great Moravia 2014: Denmark submits a claim for the North Pole to the UN 2009: Greenlandic Self-Governance after a referendum 1973–2022: Dispute with Canada over sovereignty of Hans Ø 1948: Faroe Islands granted home rule 1940–1945: German occupation 1920: Northern Schleswig (Sønderjylland) re-united with Denmark 1918: Independence of Iceland 1917: Denmark's last tropical colony, sold to United States 1864: Schleswig, Holstein & Lauenburg is lost to Prussia 1863– : House of Glücksburg 1849: New constitution with elected parliament 1814: Norway becomes independent with new constitution.
exercises supremacy over Norway Country re-united under Gorm the Old & Harald Bluetooth The decades from the 890s to the 930s are only sparse documented in written sources.
However, in June 1871, John Bates Thurston, the British honorary consul, persuaded the Fijian chiefs to accept a constitutional monarchy with Cakobau as the King, but with real power in the hands of a cabinet and legislature dominated by Australian settlers.
Fiji was settled first by the Lapita culture, around 1,500–1,000 years BC, followed by a large influx of people with predominantly Melanesian genetics about the time of the beginning of the Common Era.
[citation needed] Since 2.2 million BC, India has been settled starting with Hominins who were from Africa by the expansion of civilization with the Madrasian and Soanian cultures.
For 700 years, it was a de facto territorial extension of the capital of the Roman Republic and Empire, and for a long time experienced a privileged status and was not converted into a province.
1963–1964: Kenya (monarchy) 1920–1963: Colony and Protectorate of Kenya, part of the British Empire 1895–1920: East Africa Protectorate, part of the British Empire c.1st century AD: The Kenyan coast had served host to communities of ironworkers and communities of Bantu subsistence farmers, hunters, and fishers who supported the economy with agriculture, fishing, metal production, and trade with foreign countries.
1947–1979: Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands 1919–1947: South Seas Mandate 1914–1919: Imperial Japanese Navy occupation 1899–1914: Part of German New Guinea 1574–1899: Part of the Captaincy General of the Philippines 1940-1991: RSS of Moldova 1924-1940: Moldavian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic 1941-1944: Governorate of Transnístria 1881-1947: Kingdom of Romania 1917-1918: Moldovian Democratic Republic 1873-1918: Russian Empire 1346-1859: Moldavia 1911: Constitution of Monaco Sixth Coalition 1814: part of French Empire 1297-1814: House of Grimaldi (under the sovereignty of the Republic of Genoa) Grimaldi Man Grimaldi Manis the name formerly given to two human skeletons of the Upper Paleolithic discovered in Italy in 1901.
The vast transcontinental empire connected the East with the West, and the Pacific to the Mediterranean, in an enforced Pax Mongolica, allowing the exchange of trade, technologies, commodities, and ideologies across Eurasia.
Since 1.3 Million BC, humans have been settled in Morocco as demonstrated by the discovery of Stone Age hand-axe manufacturing site found at Casablanca in 2021.
Aruba, Curaçao, the Netherlands, and Sint Maarten are the constituent countries of the Kingdom) 1940–1945: Occupied by Nazi Germany establishing as Dutch government-in-exile, a member of the allies during WWII.
One of its most visible legacies is Bahla Fort, a large complex of mud-brick buildings on stone foundations that is registered as a UNESCO world heritage site.
1493: Arawak and Taino peoples 1739: Brief occupation by the Papal States 1503: Brief occupation by Rimini 1243: The people of San Marino established the positions of Captains Regent (Capitani Reggenti) as a joint heads of state Before 1243: Part of the Roman Empire[citation needed] 1485-1975: Portuguese São Tomé and Príncipe 1926–1932: Kingdom of Hejaz and Nejd, a dual monarchy that was the precursor to the modern day Saudi Arabia 1916–1925: Kingdom of Hejaz (Not recognized by the Ottoman Empire, last Ottoman troops evicted from Medina by Kingdom of Hejaz in 1919) 1921–1926: Sultanate of Nejd (Third Saudi State) 1916–1923: Sheikdom of Upper Asir 1913–1921: Emirate of Nejd and Hasa (Third Saudi State) 1909–1930: Idrisid Emirate of Asir 1902–1913: Emirate of Riyadh (Third Saudi State) 1836–1921: Emirate of Jabal Shammar 1824–1891: Emirate of Nejd (Second Saudi State) 1818–1824: Diriyah became part of the Egypt Eyalet, part of the Ottoman Empire 1814–1916: Sharifate of Mecca, part of the Ottoman Empire 1744–1818: Emirate of Diriyah (First Saudi State), unified all Arabian Peninsula (except Yemen and Oman) 1670–1790: Eastern Arabia, ruled by the Khalidi Emirate 1633–1934: Principality of Najran 1551–1670: Eastern Arabia, part of the Ottoman Empire 1521–1551: Al-Muntafiq, an Arab tribal confederation, successfully occupied al-Ahsa and al-Qatif (eastern Saudi Arabia today) 1517–1804: Sharifate of Mecca, part of the Ottoman Empire 1260–1517: Sharifate of Mecca, part of the Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt 1400–c.1521: Jabrids (Bahrain) rules coastal areas in Eastern Arabia.
Shortly before the advent of Islam, apart from urban trading settlements (such as Mecca and Medina), much of what was to become Saudi Arabia was populated by nomadic pastoral tribal societies.
The east coast was a territory of the Sassanid Empire By the late Bronze Age, a historically recorded people and land (Midian and the Midianites) in the north-western portion of Saudi Arabia are well-documented in the Bible.
Syria is part of the Fertile Crescent, and since approximately 10,000 BCE it was one of the centers of Neolithic culture (PPNA) where agriculture and cattle breeding appeared for the first time in the world.
698-750: Umayyad Caliphate 590-698: Exarchate of Africa 534-590: Praetorian Prefecture of Africa 435-534: Vandal Kingdom 146 BC-435: Roman Tunisia 12th C.- 146 BC: Ancient Carthage 12th C.-North African culture 1920–1923: Ottoman Empire, occupied by Greece, Italy, France, United Kingdom and Armenia (Treaty of Sèvres) (Republican Turks, led by General Mustafa Kemal Atatürk initiate the Turkish War of Independence to expel foreign occupation troops and at the same time wage a civil war against Turkish monarchists, seen as collaborationists by the republicans).
The eastern regions falls under the rule of the Median Empire 707 BCE–609 BCE: Divided in many states, like Lydia, Lycia, Phrygia, Lycaonia, Mushki, etc.
Troy was one of the members of the confederation c.2000 BCE–1600 BCE: The territory that today is Turkey was inhabited by Hattian, Hittite, Hurrian, Luwian and Anatolian tribes.
The small state of Pala was established c.2550 BCE–2000 BCE: The territory that today is Turkey was inhabited by Hattian, Hurrian and Anatolian tribes c.3500 BCE–2550 BCE: The territory that today is Turkey was inhabited by Hattian and Hurrian tribes From 10,000 BC humans has been settled making first states as Indo-Europeans, including Phrygia and Thrace.
At the end of the 7th century, most Bulgar tribes migrated in several directions and the remains of their state were absorbed by the Khazar Khaganate (650–969) c.400 AD: the Antes Union was located in the territory of what is now Ukraine.
From 12,000 BC humans has been settled stating with tribes, chiefdoms and confederations,[120][121] including Caledonians, Caereni, Carnonacae, Cat, Cornovii, Creones, Damnonii, Decantae, Lugi, Maeatae, Novantae, Picts, Selgovae, Scoti, Smertae, Taexali, Vacomagi, and Venicones.
Examples are the Mississippian cultures (the largest urban site of these peoples, Cahokia, may have reached a population of over 20,000), Puebloans, the Iroquois Confederacy, Apaches, Navajos, Cherokees, etc.
The war only comes to an end with diplomatic intervention of the United Kingdom, which establishes Uruguay as an independent nation and buffer state between Argentina and Brazil via the 1828 Treaty of Montevideo).
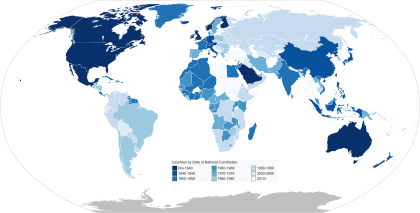
|
Pre-1940
1940–1949
1950–1959
|
1960–1969
1970–1979
1980–1989
|
1990–1999
2000–2009
2010–present
|