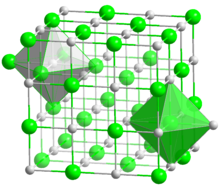
Lithium iodide
When exposed to air, it becomes yellow in color, due to the oxidation of iodide to iodine.
It is also the standard electrolyte in artificial pacemakers[6] due to the long cycle life it enables.
For example, it can be used to convert methyl esters to carboxylic acids:[9] Similar reactions apply to epoxides and aziridines.
Inorganic iodine solutions suffered from hyperosmolarity and high viscosities.
[10] It is also useful in MALDI imaging mass spectrometry of lipids by adding lithium salts to the matrix solution [11]