MAVEN
[4] The name is an acronym for "Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution" while the word maven also denotes "a person who has special knowledge or experience; an expert".
The probe is analyzing the planet's upper atmosphere and ionosphere to examine how and at what rate the solar wind is stripping away volatile compounds.
[9] On 1 October 2013, only seven weeks before launch, a government shutdown caused suspension of work for two days and initially threatened to force a 26-month postponement of the mission.
[12] The goal of MAVEN is to determine the history of the loss of atmospheric gases to space, providing answers about Martian climate evolution.
[14] In October 2014, as the spacecraft was being fine-tuned to start its primary science mission, the comet Siding Spring was also performing a close flyby of Mars.
[17] In June 2015, the science phase was extended through September 2016, allowing MAVEN to observe the Martian atmosphere through the entirety of the planet's seasons.
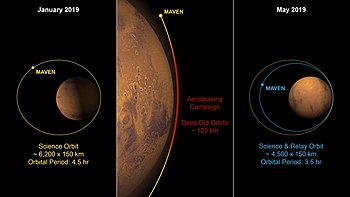
[20] On 5 April 2019, the navigation team completed a two-month aerobraking maneuver to lower MAVEN's orbit and enable it to better serve as a communications relay for current landers as well as the rover Perseverance.
This was put into place in April 2022 and completed by May 28, 2022, but during this period, MAVEN could not be used for scientific observations or to relay communications to Earth from the rovers Curiosity and Perseverance and the Insight lander.
[25] NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory provided an Electra ultra high frequency (UHF) relay radio payload which has a data return rate of up to 2048 kbit/s.
In the extended mission period of up to ten years, MAVEN will provide UHF relay service for present and future Mars rovers and landers.
The hydrogen, as the lightest element, then tends to rise far up to the highest levels of the Martian atmosphere, where several processes can strip it away into space, to be forever lost to the planet.
[39] On 5 November 2015, NASA announced that data from MAVEN shows that the deterioration of Mars's atmosphere increases significantly during solar storms.
[45] The NGIMS instrument was able to directly sample dust from this Oort Cloud comet, detecting at least eight different types of metal ions.
[47] In September 2017, NASA reported a temporary doubling of radiation levels on the surface of Mars, as well as an aurora 25 times brighter than any observed earlier.
[48] The observation provided insight into how changes in radiation levels might impact the planet's habitability, helping NASA researchers understand how to predict as well as mitigate effects on future human Mars explorers.


MAVEN · Mars · Earth · Sun

MAVEN · Mars