Maemo
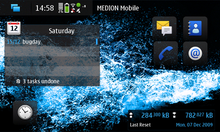
The Maemo 5 user interface is slightly different; the menu bar and info area are consolidated to the top of the display, and the four desktops can be customized with shortcuts and widgets.
The dashboard is accessed via the upper left icon and shows all the running applications, in a manner similar to the Exposé feature in Apple's Mac OS X operating system.
Data can be synchronized with a PC via a USB connection, and the user's files can be accessed using the standard Removable Storage Device protocol.
[19] Flashing remains available as a way to start over from scratch with a clean installation (much like formatting a hard drive and reinstalling an operating system on a PC).
[20] The quick start guide for developers warns that Maemo security concentrates on preventing remote attacks (e.g. by wireless networking and Bluetooth).
[21] Maemo employs a numeric security code as a way to lock the device's controls and display independently of the root password, to help prevent unauthorised access.
[24] BusyBox, a software package for embedded and mobile devices, replaces the GNU Core Utilities used in Debian-proper to reduce memory usage and storage requirements (at the expense of some functionality).
Some notable software includes: Other media types, such as the audio format .OGG, can be added with the use of community plug-ins.
Software can be developed in C using the Maemo SDK, Java (which is supported by the Jalimo JVM),[35] Python, Ruby, Mono, Vala, Perl and Pascal.
The Maemo SDK is based around the Debian-oriented Scratchbox Cross Compilation Toolkit, which provides a sandbox environment in which development may take place.
[38] Although the highly optimized, hardware-specific nature of Maemo renders its operation on non-Internet tablet hardware very difficult, most of the important non-proprietary parts of the operating system, along with some of the available third-party applications, are actively being packaged for Debian and are available for use on other distributions, which will open up a large range of other hardware options.
It came bundled with the Opera web browser, Flash 6, basic email and RSS clients, audio and video players, PDF and image viewers, a graphical Advanced Packaging Tool, front-end (dubbed simply "Application manager"), and a variety of simple games and utilities.
[42] The update featured improved performance and stability, a built-in Google Talk client, a refreshed look, and a new full-screen finger keyboard.
OS2008 was released with the N810 in November 2007, based on Linux 2.6.21, and featuring MicroB, a new Mozilla-based web browser that replaces Opera.
[48] Major features include significant improvements to the built-in Application manager, incremental operating system upgrades without reflashing ("Seamless Software Update", SSU), Modest as the default mail client, and a new version of the MicroB browser with better performance and some interface improvements (though still based on the same Gecko release as Chinook's MicroB).
[54][55] Maemo 5 comes with new hardware, the Nokia N900 featuring a Texas Instruments OMAP3 SoC, with an HSPA modem and HD camera, which provides significant improvements in speed, 3D acceleration, and media playback.
[57] Unlike most smartphones, the end-user is able to gain root access by installing an application, such as the "rootsh",[58] and then issuing the appropriate command in the terminal in Maemo 5.
[63] For example, Nokia has launched a contest at the onedotzero festival in London called PUSH N900 aimed at designers, artists, hackers and modders.
It is a modernised and liberated version of Maemo 5, rebased on top of Devuan with a mainline Linux kernel.
[67] The latest release supports phone calls and SMS messages on a number of devices, including the Nokia N900 (some integration and bug fixes remain) and the Motorola Droid 4, as announced in the project's Five-year anniversary blog post.
Unlike other distributions, Maemo Leste targets devices where it can be used with upstream Linux kernels - to offer proper updates to both functionality and security.
The operating system aims to be entirely open source, and even re-implements certain closed components that were present in Maemo Fremantle.
Maemo Leste is entirely community-developed, and its developers are active on #maemo-leste connect on the Libera Chat IRC network.
The Hacker Editions allow 770 users to access the latest Internet Tablet OS releases and third-party software, although due to the 770's hardware limitations and the increased CPU requirements of OS2008, performance is inferior to that of OS2007 HE in most areas.
It is still using the APT package manager for applications, but the graphical user interface and major parts of the system were improved, rewritten from scratch or rebased on top of Meego frameworks.
It is heavily using the Qt libraries instead of GTK+/Hildon, and introduced a new UI paradigm based on Swipe gestures, done from the edge of the screen.
[79][80] After problems with the original Meego project, Nokia decided to rename Harmattan to Meego/Harmattan and shipped their N9 with this OS.
Mer is a completely free and open-source software distribution targeting mobile and embedded systems, first developed for reimplementing Maemo in the open, and then rebased on top of the MeeGo tools.
In January 2008, Nokia began the process of acquiring Trolltech, the developer of the Qt application framework.