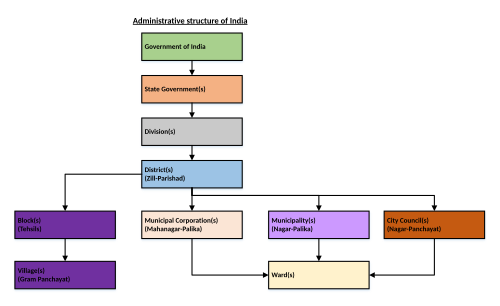
Municipal corporation (India)
A municipal corporation is a type of local government in India which administers an urban area having a population of one million or more.
[citation needed] The 74th Amendment Act defined the formations of urban local governments and their activities.
These names include Nagar Nigam (in Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Bihar, Jharkhand, Rajasthan, and Haryana), Nagara Nigama (in Punjab), Mahanagar Palika (in Goa and Maharashtra), Mahanagara Palike (in Karnataka), Mahanagar Seva Sadan (in Gujarat), Pouro Nigom (in Assam), Mahānagara Nigama (in Odisha), Pouro Nigam (in West Bengal), Pur Porishod (in Tripura), Nagar Palika Nigam (in Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh), Nagara Paalaka Samstha or Mahaanagara Paalaka Samstha (in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana), Nagara Sabha (in Kerala) and Maanagaraatchi (in Tamil Nadu).
In addition to the councillors elected from the wards, the legislature of a state may also choose to make provisions for the representation of persons having special knowledge or experience in municipal administration, the MPs or MLAs representing the constituencies which comprise wholly or partly the municipal area, and/or the commissioners of additional committees that the state may have constituted.
These officials are tasked with the day-to-day operations, implementing policies, and ensuring the efficient delivery of essential services.
Executive officers monitor the implementation of all the programs related to planning and development of the corporation with the coordination of mayor and councilors.
The municipal corporations consists departments like health, general administration, revenue, engineering, town planning, welfare, education, etc.
Corporations may be entrusted to perform functions and implement schemes including those in relation to the matters listed in the Twelfth Schedule.