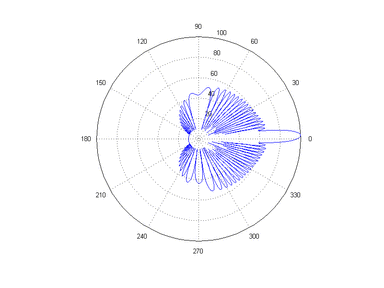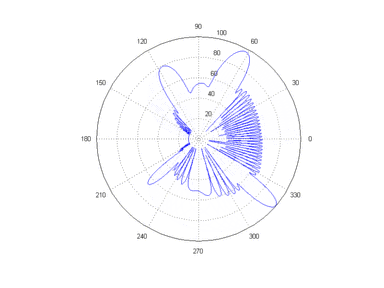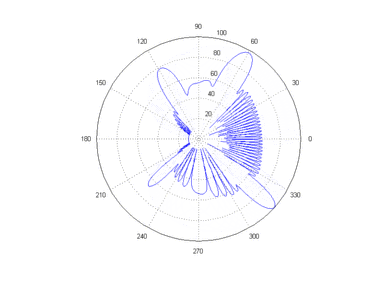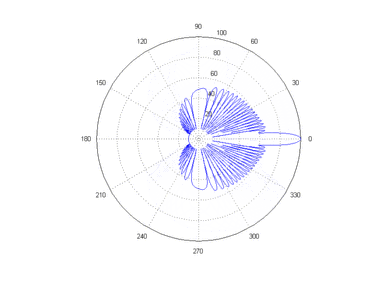
Main lobe
The other lobes are called "sidelobes", and usually represent unwanted radiation in undesired directions.
The sidelobe in the opposite direction from the main lobe is called the "backlobe".
The beamwidth of the antenna is the width of the main lobe, usually specified by the half power beam width (HPBW), the angle encompassed between the points on the side of the lobe where the power has fallen to half (-3 dB) of its maximum value.
The concepts of main lobe and sidelobes also apply to acoustics and optics, and are used to describe the radiation pattern of optical systems like telescopes, and acoustic transducers like microphones and loudspeakers.
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C.