Medicago polymorpha
It forms a symbiotic relationship with the bacterium Sinorhizobium medicae, which is capable of nitrogen fixation.
It is found in lawns as well, where its burrs are able to cling to the clothing or fur of any species that pass near it, thus facilitating geographic spread via these seed capsules.
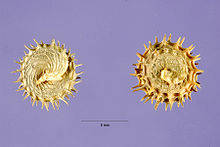
It makes a poor lawn in the late summer, when the leaves have yellowed and fruit sets into the 7 mm seed heads that are covered with hooked prickles.
Full grown plant stems are up to 2 feet (60 cm) long, and usually sprawl along and/or under the ground.
Bloom takes place from March to June in the plant's native territory.
The burred fruiting bodies can be quite difficult to remove from softer fabrics, such as fleeces and knitted socks.
[2][3][4] The plant is edible and consumed as a vegetable in China, primarily in Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Shanghai.
[5] Its Chinese culinary names include 草頭 (Wu tsho-doe, Mandarin Pinyin cǎo tóu), 金花菜 (Wu cin-hau tse, Mandarin Pinyin jīn huā cài), 三叶菜 (sān yè cài) and 秧草 (yāng cǎo), while 南苜蓿 (nán mùxu) is its scientific name.