Meta-process modeling
Its main concern is to improve process models and to make them evolve, which in turn, will support the development of systems.
[2] "The focus has been to increase the level of formality of process models in order to make possible their enactment in process-centred software environments".
Since this experience is not formalised and is, consequently, not available as a fund of knowledge, it can be said that these process models are the result of an ad hoc construction technique.
Clearly, generation and modifiability relate to the process management policy adopted (see Usage World).
Instantiation and assembly, by promoting modularization, facilitate the capitalisation of good practice and the improvement of given process models.
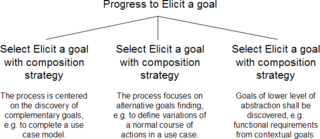
Rolland (1998) lists two selection strategies:[2] For the assembly technique to be successful, it is necessary that process models are modular.
This potential is realised when a generation technique is defined whose application results in the desired process model.
Often the instantiation technique "has been utilised to build the repository of Computer Aided Method Engineering environments".
The CREWS-L'Ecritoire method represents a methodical approach for Requirements Engineering, "the part of the IS development that involves investigating problems and requirements of the users community and developing a specification of the future system, the so-called conceptual schema.".
The approach is based on the notion of a labelled graph of intentions and strategies called a map as well as its associated guidelines.
The map contains a finite number of paths, each of them prescribing a way to develop the product, i.e. each of them is a process model.
Furthermore, the approach is meant to allow the dynamic adjunction of a path in the map, i.e. adding a new strategy or a new section in the actual course of the process.
[3] A guideline "helps in the operationalisation of the selected intention";[3] it is "a set of indications on how to proceed to achieve an objective or perform an activity.
"[33] The description of the guidelines is based on the NATURE project's contextual approach[9][34][35] and its corresponding enactment mechanism.
Colette Rolland describes the meta-model as follows:[3] (Meta-intentions are in bold, meta-strategies in italic – in green in the map.)
The following table displays the stepwise trace of the process to elicit requirements for the recycling machine (from[3] ):