Mexican Americans
[23] It is estimated that approximately 10% of the current Mexican-American population are descended from residents of the Spanish Empire and later Mexico, which preceded the acquisition of their territories by the United States; such groups include New Mexican Hispanos, Tejanos of Texas, and Californios.
[31] The Mexican government became concerned about the increasing volume of Anglo-American immigration and restricted the number of settlers from the United States allowed to enter Texas.
With relations between Californios and Americans quickly souring, Fremont returned to Alta California, where he encouraged European-American settlers to seize a group of Castro's soldiers and their horses.
Tens of thousands of miners and associated people arrived during the California gold rush, and their activities in some areas meant the end of the Californios' ranching lifestyle.
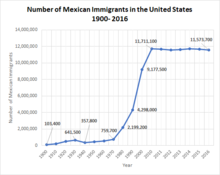
[50] The lack of agricultural laborers due to increases in military drafts for World War II opened up a chronic need for low-wage workers to fill jobs.
Both citizens and noncitizens identify ethnic issues as the key problem that Mexican Americans face, highlighting the need for stronger community and political organization.
By the early 21st century, the states with the largest percentages and populations of Mexican Americans are California, Arizona, New Mexico, Texas, Colorado, Nevada and Utah.
Though there is no simple explanation, it is possibly some combination of assortative mating, changes in migration patterns over time (with more recent immigrants coming from areas of more concentrated Indigenous communities), population growth and other unexamined factors.
[76] For instance, a 2006 study conducted by Mexico's National Institute of Genomic Medicine (INMEGEN), which genotyped 104 samples, reported that Mestizo Mexicans are 58.96% European, 35.05% Amerindian, and 5.03% African.
[70] A 2012 study published by the Journal of Human Genetics found the deep paternal ancestry of the Mexican Mestizo population to be predominately European (64.9%) followed by Amerindian (30.8%) and African (5%).
The US Supreme Court ruling in Hernandez v. Texas case held that "nationality" groups could be protected under the Fourteenth Amendment, and it became a landmark in the civil rights history of the United States.
[85][86] While Mexican Americans served in all-White units during World War II, many Mexican–American veterans continued to face discrimination when they arrived home; they created the G.I.
The 1968 Los Angeles, California school walkouts expressed Mexican-American demands to end de facto ethnic segregation (also based on residential patterns), increase graduation rates, and reinstate a teacher fired for supporting student political organizing.
[91] Many organizations, businesses, and homeowners associations and local legal systems had official policies in the early 20th century to exclude Mexican Americans in a racially discriminatory way.
During The Great Depression, the United States government sponsored a Mexican Repatriation program which was intended to encourage people to voluntarily move to Mexico, but thousands were deported against their will.
Testing these hypotheses with data from the US Census and national and Los Angeles opinion surveys, Citrin et al. (2007) show that Latinos generally acquire English and lose Spanish rapidly beginning with the second generation, and appear to be no more or less religious or committed to the work ethic than native-born non-Mexican American whites.
Their longitudinal analysis of seven hundred Mexican, Puerto Rican, and Cuban immigrants followed from 1990 to 1995 finds broad support for hypotheses derived from the classical account of assimilation into American society.
The 1968 Los Angeles school walkouts expressed Mexican American demands to end segregation, increase graduation rates, and reinstate a teacher fired for supporting student organizing.
The bracero program, which began in 1942 and officially ended in 1964, allowed them temporary entry into the United States as migrant workers in farms throughout California and the Southwest.
[153] Various reasons for the inferiority of the education given to Mexican American students have been listed by James A. Ferg-Cadima including: inadequate resources, poor equipment, unfit building construction.
[153] Some have interpreted the shortened school year as a "means of social control" implementing policies to ensure that Mexican Americans would maintain the unskilled labor force required for a strong economy.
By limiting the number of days that Mexican Americans could attend school and allotting time for these same students to work, in mainly agricultural and seasonal jobs, the prospects for higher education and upward mobility were slim.
Although they are segregated from the general population, hubs have helped many immigrants to acclimate to the United States, learn English, accumulate wealth, and once they are established, move into mainstream society.
The official story is that Salazar was killed by a tear gas canister fired by a member of the Los Angeles County Sheriff's Department into the Silver Dollar Café at the conclusion of the National Chicano Moratorium March.
[157] It is important to know that the parents of Mexican American students frequently display their involvement through untraditional methods; such as, consejos, home-base practices, and high academic expectations.
A mother's role teaches their child the importance of everyday tasks such as knowing how to cook, clean and care for oneself to be independent and also to help out around the house.
The study found a higher level of academic achievement among 8th grade Mexican American students and parents who had high educational aspirations for their children (Keith & Lichtman, 1995).
Additional research done by Carranza, You, Chhuon, and Hudley (2009)[162] added support to the idea that high parental expectations were associated with higher achievement levels among Mexican American students.
Additionally, Carranza et al. noted that among females, those who perceived that their parents expected them to get good grades tended to study more and have higher academic aspirations (2009).
[213] The largest populations of Mexicans are situated in the following metropolitan areas (Source: 2020 ACS 5-Year Estimates):[217][218][219] Diabetes refers to a disease in which the body has an inefficiency of properly responding to insulin, which then affects the levels of glucose.