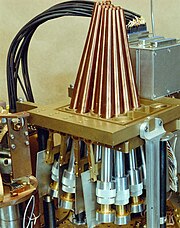
Millimeter Anisotropy eXperiment IMaging Array
For the first flight it took data from about 0.3 percent of the sky of the northern region near the Draco constellation.
A bolometer array consisting of sixteen NTD-Ge thermistors measured the incident radiation.
The other camera was mounted in the primary focus and gave an accuracy of half an arcminute for stars brighter than 6th magnitude.
By the end of the year 2000 the experiment had provided the most accurate measurements of the Cosmic microwave background (CMB) fluctuations on small angular scales.
The measurement of the flatness of the Universe also confirmed a major prediction of inflationary cosmology, although BOOMERang was the first to discover this.