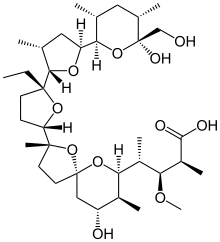
Monensin
[5][6] Monensin A is able to transport these cations across lipid membranes of cells in an electroneutral (i.e. non-depolarizing) exchange, playing an important role as an Na+/H+ antiporter.
Recent studies have shown that monensin may transport sodium ion through the membrane in both electrogenic and electroneutral manner.
[7] This approach explains ionophoric ability and in consequence antibacterial properties of not only parental monensin, but also its derivatives that do not possess carboxylic groups.
It blocks intracellular protein transport, and exhibits antibiotic, antimalarial, and other biological activities.
[8] The antibacterial properties of monensin and its derivatives are a result of their ability to transport metal cations through cellular and subcellular membranes.