Obesity-associated morbidity
Peter Muennig, a professor in the Department of Health Policy and Management at Columbia University,[8] has proposed that obesity-associated medical conditions may be caused "not from adiposity alone, but also from the psychological stress induced by the social stigma associated with being obese".
[11] Abdominal obesity is associated with cardiovascular diseases including angina and myocardial infarction.
[13] In 2008, European guidelines concluded that 35% of ischemic heart disease among adults in Europe is due to obesity.
[15][verification needed] More than 85% of those with hypertension have a BMI greater than 25, although diet is probably a more important factor than body weight.
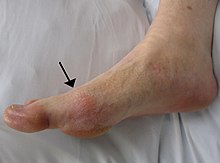
[20][21] Obesity is associated with the incidence of stretch marks, acanthosis nigricans, lymphedema, cellulitis, hirsutism, and intertrigo.
[22][23] The link between obesity and type 2 diabetes is so strong that researchers in the 1970s started calling it "diabesity".
This is primarily due to excess estrogen interfering with normal ovulation in females[15] and altering spermatogenesis in males.
[15][33] A review in 2013 came to the result that obesity increases the risk of oligospermia and azoospermia in males, with an of odds ratio 1.3.
[33] Excess body fat in morbid obesity can, in some cases, completely obscure or "bury" the penis.
[43] The risk of carpal tunnel syndrome is estimated to rise 7.4% for each 1 kg/m2 increase of body mass index.
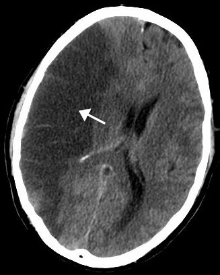
[45] Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, or unexplained high pressure in the cranium, is a rare condition that can cause visual impairment, frequent severe headache, and tinnitus.
[51] For those undergoing surgery for cancer, obesity is also associated with an increased risk of major postoperative complications compared with those of "normal" weight.
[15] However, it is possible that obesity is caused by depression (due to reduced physical activity or, in some people, increases in appetite).
[53] Similarly, weight loss through bariatric surgery is associated with increased risk of suicide.
[56] People who are obese also experience fewer educational and career opportunities, on average earn a lesser income,[57] and generally receive poorer health care and treatment[5] than individuals of "normal" weight.
[58] It is believed that a systemic pro-inflammatory state induced by some causes of obesity may contribute to airway inflammation, leading to asthma.
[60] Obesity significantly reduces and stiffens the functional lung volume, requiring specific strategies for respiratory management under general anesthesia.
[68] Obese individuals are twice to four times more likely to have lower back pain than their "normal" weight peers.
[75] Obese male individuals can experience erectile dysfunction, and weight loss can improve their sexual functioning.