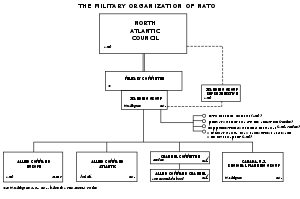
Structure of NATO
[2][3] Below that the Secretary General of NATO directs the civilian International Staff, that is divided into administrative divisions, offices and other organizations.
Also responsible to the NAC, DPPC, and NPG are a host of committees that supervise the various NATO logistics and standardisation agencies.
The DPC was a former senior decision-making body on matters relating to the integrated military structure of the Alliance.
Its responsibilities absorbed by the North Atlantic Council and the Defence Policy and Planning Committee (DPPC).
Thus the Secretariat provides secretaries to all the Council's principal committees and working groups - apart from those of a strictly technical nature - and ensures co-ordination between them.
.. On the Staff side there are three main divisions corresponding to the three principal aspects of NATO's work, each under an Assistant Secretary General.
The Divisions' tasks are to prepare, in close touch with delegations, proposed action in their respective fields for consideration by the appropriate committee or by the Council.
The Standing Group was abolished during the major reform of 1967 that resulted from France's departure from the NATO Military Command Structure.
[10] This was due to the two states' geographic distance from the LANDSOUTH headquarters, as well as disagreements over which nation should be the overall commander for their ground forces.
Previously Commander-in-Chief Portsmouth had controlled multinational naval operations in the area under WUDO auspices.
Headquarters Allied Forces Central Europe was moved from the Chateau de Fontainebleau outside Paris to Brunssum, in the Netherlands.
In 1995 NATO began a Long Term Study to examine post-Cold War strategy and structure.
The Defence Planning Committee was a former senior decision-making body on matters relating to the integrated military structure of the Alliance.
On 12 June 2003 NATO ministers announced an end to the decades-old structure of a command each for the Atlantic and Europe.
[25] The alliance created several NATO Rapid Deployable Corps and naval High Readiness Forces (HRFs), which all report to Allied Command Operations.
[30] Directly responsible to SACEUR is the NATO Airborne Early Warning Force at NATO Air Base Geilenkirchen in Germany where a jointly funded fleet of Boeing E-3 Sentry Airborne early warning and control radar (AWACS) aircraft are located.
The Boeing C-17 Globemaster IIIs of the Strategic Airlift Capability, which became fully operational in July 2009, are based at Pápa airfield in Hungary.
In early 2015, in the wake of the War in Donbass, meetings of NATO ministers decided that Multinational Corps Northeast would be augmented so as to develop greater capabilities, to, if thought necessary, prepare to defend the Baltic States, and that a new Multinational Division Southeast would be established in Romania.
[33] Headquarters Multinational Division South – East (HQ MND-SE) is a North Atlantic Council (NAC) activated NATO military body under operational command (OPCOM) of Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR) which may be employed and deployed in peacetime, crisis and operations.
[34] The division is tasked to coordinate the four NATO Enhanced Forward Presence battlegroups and to carry out Article 5 collective defence activities.
[41] In August 1953 it was tasked to '..(a) Prepare, approve and forward to the Military Committee, through the Standing Group, plans for and other material pertaining to, the defense of the Canada-U.S.
[42] The NATO Handbook stated in 1990s editions that it was responsible for the defence of the US-Canada area and meets alternatively in Washington, D.C., and Ottawa.