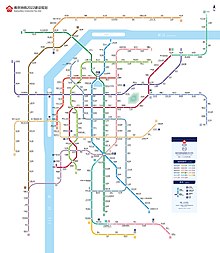
Nanjing Metro
Proposals for a metro system serving Nanjing first began in 1984, with approval by the State Planning Commission granted in 1994.
Future expansion plans include 30 lines set to open within the next few years, with several more awaiting approval to begin construction.
The initial section of Line 1 from Maigaoqiao to Xiaohang received final official approval in 1999.
A western extension of Line 1 from Xiaohang to a newly built stadium was fast tracked after Nanjing won hosting the National Games.
Line 1's initial section and the western extension started trial operations on September 3, 2005, running from Maigaoqiao to Olympic Stadium with 16 stations and a total length of 21.72 kilometers (13.50 mi).
The line starts at Maigaoqiao in the north, heading southwards to CPU (China Pharmaceutical University).
The construction of Line 1 began in the year 2000 and was inaugurated on September 3, 2005, with 16 stations and a length of 21.72 kilometers (13.50 mi).
This line, with a north–south orientation, started operation on April 1, 2015[26] and is 44.9 kilometres (27.9 mi) in length with 29 stations.
[38] The first phase from Nanjing South to Lukou International Airport started construction on December 27, 2011, and finished in 2014.
It starts from Nanjing South Railway Station and heads west, crossing the Yangtze River on the cantilever along the edge of Dashengguan Yangtze River bridge together with high-speed rail trains, before terminating at the Gaojiachong station in Qiaolin, southwest of Pukou District.
The line will feature passing loops at select stations to allow for distinct express and local services.
[46] Line S6 or the Nanjing-Jurong Intercity Railway is a 43.7 kilometers (27.2 mi) connecting suburban Nanjing with neighboring Jurong opened on 28 December 2021.
It uses B size trains in 4 car sets that are capable of running up to 100 kilometers per hour (62 mph).
Upon opening on December 30, 2017, Nanjing became the first city in mainland China where every district is accessible by metro.
In the future, it will become an important line within the main city to connect the central Hexi, Xiaguan and Xinzhuang areas.
The regional line is of great significance to the development of Hexi New City and the upgrading and reconstruction of the Xiaguan area.
[64] The list of stations: Danxialu, Caohouxun, Nanjing Railway Station, Zhongyangmen, Chenghecun, Daqiaonanlu, Xiaguan, Agricultural Trade Centre, Dinghuaimendajie, Longjiang, Guanziqiao, Hanzhongmendajie, Shuiximendajie, Qinghelu, Lüboyuan and Binjianggongyuan.
[65] In the southern extension of Phase 2, Line 9 is expected to be extended all the way to Banqiao in the far south west of Nanjing.
The Nanjing Metro Phase III construction plan was submitted to the National Development and Reform Commission in 2024.
[70] Apart from one-way tickets, fares can be paid with the Nanjing Public Utility IC Card, or Jinlingtong (Chinese: 金陵通; pinyin: Jīnlíngtōng).
It can be purchased for a refundable fee of 25 yuan (about 3.8 dollars) and refilled at ticket booths inside the metro stations as well as many collaborative convenience stores throughout the city.
An NFC version of the card is free of charge by applying from the iPhone's Wallet app.
For Line 1, Siemens Transportation Systems (TS) was awarded the supply contract in November 2002.
For Line 2, Siemens Transportation Systems (TS) and its local partner Nanjing Research Institute of Electronic Technology (NRIET) have been awarded to supply the signaling system after signing a contract (about 25 million Euro).
Technologies used include Trainguard MT, Vicos OC 501, Sicas ECC and Az S 350 U axle counting system.