Narayana number
form a triangular array of natural numbers, called the Narayana triangle, that occur in various counting problems.
They are named after Canadian mathematician T. V. Narayana (1930–1987).
The Narayana numbers can be expressed in terms of binomial coefficients: The first eight rows of the Narayana triangle read: (sequence A001263 in the OEIS) An example of a counting problem whose solution can be given in terms of the Narayana numbers
pairs of parentheses, which are correctly matched (known as Dyck words) and which contain
, since with four pairs of parentheses, six sequences can be created which each contain two occurrences the sub-pattern (): From this example it should be obvious that
, since the only way to get a single sub-pattern () is to have all the opening parentheses in the first
positions, followed by all the closing parentheses.
distinct nestings can be achieved only by the repetitive pattern ()()()…().
More generally, it can be shown that the Narayana triangle is symmetric: The sum of the rows in this triangle equal the Catalan numbers: The Narayana numbers also count the number of lattice paths from
, with steps only northeast and southeast, not straying below the x-axis, with
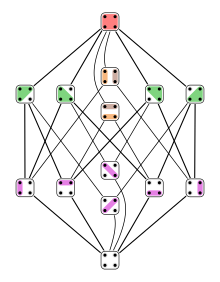
The following figures represent the Narayana numbers
This sum coincides with the interpretation of Catalan numbers as the number of monotonic paths along the edges of an
grid that do not pass above the diagonal.
The number of unlabeled ordered rooted trees with
This is analogous to the above examples: In the study of partitions, we see that in a set containing
elements, we may partition that set in
Furthermore, the number of ways to partition a set into exactly
Both of these concepts are a bit off-topic, but a necessary foundation for understanding the use of the Narayana numbers.
In both of the above two notions crossing partitions are accounted for.
To reject the crossing partitions and count only the non-crossing partitions, we may use the Catalan numbers to count the non-crossing partitions of all
The generating function for the Narayana numbers is [1]