Geography of Burkina Faso
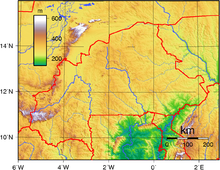
It lies between the Sahara desert and the Gulf of Guinea, south of the loop of the Niger River, mostly between latitudes 9° and 15°N (a small area is north of 15°), and longitudes 6°W and 3°E.
Most of central Burkina Faso lies on a savanna plateau, 198–305 metres (650–1,001 ft) above sea level, with fields, brush, and scattered trees.
Burkina Faso's game preserves – the most important of which are Arly, Nazinga, and W National Park—contain lions, elephants, hippopotamus, monkeys, common warthogs, and antelopes.
The larger part of the country is covered by a peneplain, which forms a gently undulating landscape with, in some areas, a few isolated hills, the last vestiges of a Precambrian massif.
The southwest of the country, on the other hand, forms a sandstone massif, where the highest peak, Ténakourou, is found at an elevation of 749 metres (2,457 feet).
The Niger's tributaries – the Béli, the Gorouol, the Goudébo and the Dargol – are seasonal streams and flow for only four to six months a year.
Further to the south, the Sudan-Guinea zone receives more than 900 millimeters (35 inches) of rain each year and has cooler average temperatures.
Burkina Faso's natural resources include manganese, limestone, marble, phosphates, pumice, salt and small deposits of gold.
[11] Current environmental issues include: recent droughts and desertification severely affecting agricultural activities, population distribution, and the economy; overgrazing; soil degradation; deforestation.
Burkina Faso is party to the following international environmental agreements: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands.