Netfilter
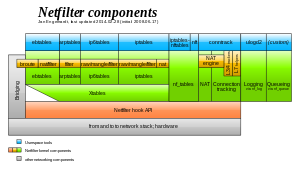
Netfilter is a framework provided by the Linux kernel that allows various networking-related operations to be implemented in the form of customized handlers.
Those functions, usually applied to the traffic in the form of filtering and modification rules, are called for every packet that traverses the respective hook within the networking stack.
In April 2004, following a crack-down by the project on those distributing the project's software embedded in routers without complying with the GPL, a German court granted Welte an historic injunction against Sitecom Germany, which refused to follow the GPL's terms (see GPL-related disputes).
In September 2007 Patrick McHardy, who led development for past years, was elected as new chairman of the coreteam.
The connection tracking and NAT subsystems are more general and more powerful than the rudimentary versions within ipchains and ipfwadm.
Netfilter modules not organized into tables (see below) are capable of checking for the origin to select their mode of operation.
[6] The main advantages over iptables are simplification of the Linux kernel ABI, reduction of code duplication, improved error reporting, and more efficient execution, storage, and incremental, atomic changes of filtering rules.
This is necessary for the in-kernel connection tracking and NAT helper modules (which are a form of "mini-ALGs") that only work reliably on entire packets, not necessarily on fragments.
Part of the reason for this is that when merely forwarding packets, i.e. no local delivery, the TCP engine may not necessarily be invoked at all.
Even connectionless-mode transmissions such as UDP, IPsec (AH/ESP), GRE and other tunneling protocols have, at least, a pseudo connection state.
The heuristic for such protocols is often based upon a preset timeout value for inactivity, after whose expiration a Netfilter connection is dropped.
IP fragmentation is dealt with the connection tracking subsystem requiring defragmentation, though TCP segmentation is not handled.
conntrack-tools is a set of user-space tools for Linux that allow system administrators to interact with the Connection Tracking entries and tables.
ipset does not make use of Netfilter hooks for instance, but actually provides an iptables module to match and do minimal modifications (set/clear) to IP sets.
Different storage algorithms (for the data structures in memory) are provided in ipset for the user to select an optimum solution.
[9] On 3 November 2013, SYN proxy functionality was merged into the Netfilter, with the release of version 3.12 of the Linux kernel mainline.
[10][11] ulogd is a user-space daemon to receive and log packets and event notifications from the Netfilter subsystems.
Netfilter also provides a set of libraries having libnetfilter as a prefix of their names, that can be used to perform different tasks from the userspace.