OECD
Empirical methods Prescriptive and policy The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; French: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, OCDE) is an intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries,[1][4] founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade.
By this time, some leading countries felt that the OEEC had outlived its purpose but could be adapted to fulfil a more global mission, which proved to be a cumbersome task.
Following several (occasionally unruly) meetings at the Hotel Majestic in Paris, which began in January 1960, a resolution was reached to create a body that would not only solve European and Atlantic economic issues, but also devise policies that could assist less developed countries.
Three countries, (Netherlands, Luxembourg, and Italy)—all OEEC members—ratified the OECD Convention after September 1961, but are nevertheless considered founding members.
Following the Revolutions of 1989, the OECD began assisting countries in Central Europe (especially the Visegrád Group) to prepare market economy reforms.
[28] In 1996, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania signed a Joint Declaration expressing willingness to become members of the OECD,[29] and Slovenia also applied for membership that same year.
[32] Romania reaffirmed in 2012 its intention to become a member of the Organisation through the letter addressed by Romanian Prime Minister Victor Ponta to OECD Secretary-General José Ángel Gurría.
The working group defined four criteria that must be fulfilled: "like-mindedness", "significant player", "mutual benefit" and "global considerations."
The working group's recommendations were presented at the OECD Ministerial Council Meeting on 13 May 2004, and on 16 May 2007, the OECD Ministerial Council decided to open accession discussions with Chile, Estonia, Israel, Russia, and Slovenia, and to strengthen cooperation with Brazil, China, India, Indonesia, and South Africa through a process of enhanced engagement.
[47] In January 2022, the OECD reported that membership talks were underway with Argentina, Brazil, Bulgaria, Croatia, Peru and Romania.
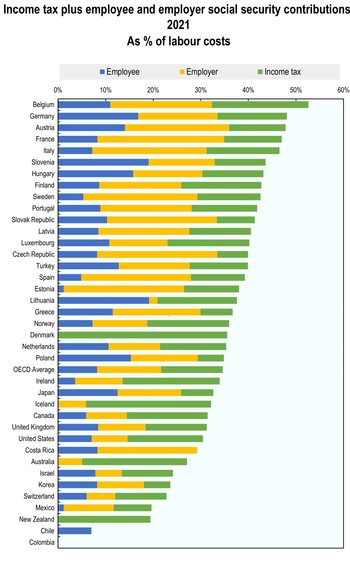
The OECD publishes and updates a model tax convention that serves as a template for allocating taxation rights between countries.
The latest version, of July 2017, incorporates the approved Actions developed under the Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) project initiated by the G20.
All the major economies agreed to pass national laws that would require corporations to pay at least 15% income tax in the countries they operate.
This new policy would end the practice of locating world headquarters in small countries with very low taxation rates.
Secretary-General Mathias Cormann of the OECD said, "This historic package will ensure that large multinational companies pay their fair share of tax everywhere.
They are recommendations providing principles and standards for responsible business conduct for multinational corporations operating in or from countries adhering to the Declaration.
[60] The online and mobile[61] editions contained news, analysis, reviews, commentaries and data on global economic, social and environmental challenges and listings of the latest OECD books.
[63] The OECD Observer was last issued in the fourth quarter of 2019, with a double edition looking ahead at artificial intelligence, and a cover leading on why statistical offices should hire a comedian.
The English edition of Shigehara's memoirs titled The Bank of Japan, the OECD, and Beyond was published by Palgrave Macmillan in September 2024.
[74][75] The OECD's structure consists of three main elements:[76] Delegates from the member countries attend committee and other meetings.
Under the direction and guidance of member governments, it also researches social changes or evolving patterns in trade, environment, education, agriculture, technology, taxation and other areas.
[81] Representatives of member and observer countries meet in specialised committees on specific policy areas, such as economics, trade, science, employment, education, development assistance or financial markets.
[115] As of January 2021, the Dutch Caribbean and the British territories of Guernsey, Jersey, the Isle of Man, Gibraltar, and Bermuda are included as part of the OECD memberships of the Netherlands and the U.K., respectively.
[35] In March 2014, the OECD halted membership talks in response to Russia's role in that year's Crimean Annexation and continuous human and civil rights abuses.
[151] The OECD operates on a two-year budget determined by member countries, with annual revenues over 700 million EUR during the most recent reporting period (2021–2022).