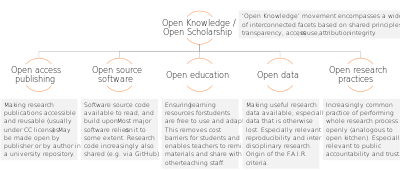
Open knowledge
[2] In the fourth volume of the Encyclopédie, Denis Diderot allowed re-use of his work in return for him having used material from other authors.
In the early twentieth century, a debate about intellectual property rights developed within the German Social Democratic Party.
With the development of the public Internet from the early 1990s, it became far easier to copy and share information across the world.
Wikipedia was founded in 2001 with the ethos of providing information which could be edited and modified to improve its quality.
The success of Wikipedia became instrumental in making open knowledge something that millions of people interacted with and contributed to.