Near-infrared window in biological tissue
[1] Within the NIR window, scattering is the most dominant light-tissue interaction, and therefore the propagating light becomes diffused rapidly.
Medical imaging techniques such as fluorescence image-guided surgery often make use of the NIR window to detect deep structures.
) is defined as the probability of photon absorption in tissue per unit path length.
Discussed below are the absorption properties of the most important chromophores in tissue.
These two different types of hemoglobin exhibit different absorption spectra that are normally represented in terms of molar extinction coefficients, as shown in Figure 1.
Its spectrum then gradually decreases as light wavelength increases.
) can then be computed as Although water is nearly transparent in the range of visible light, it becomes absorbing over the near-infrared region.
Water is a critical component since its concentration is high in human tissue.
The absorption spectrum of water in the range from 250 to 1000 nm is shown in Figure 2.
Although absorption is rather low in this spectral range, it still contributes to the overall attenuation of tissue.
Melanin is a chromophore that exists in the human epidermal layer of skin responsible for protection from harmful UV radiation.
When melanocytes are stimulated by solar radiation, melanin is produced.
[7] Melanin is one of the major absorbers of light in some biological tissue (although its contribution is smaller than other components).
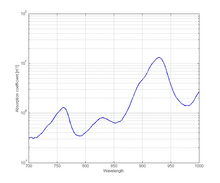
There are two types of melanin: eumelanin which is black-brown and pheomelanin which is red-yellow.
[8] The molar extinction coefficient spectra corresponding to both types are shown in Figure 3.
[9] Optical scattering occurs due to mismatches in refractive index of the different tissue components, ranging from cell membranes to whole cells.
Cell nuclei and mitochondria are the most important scatterers.
[11] Their dimensions range from 100 nm to 6 μm, and thus fall within the NIR window.
), which is defined as the probability of photon scattering in tissue per unit path length.
is the anisotropy of biological tissue, which has a representative value of 0.9.
Figure 5 shows a plot of transport scattering coefficient spectrum in breast tissue, which has a wavelength dependence of
A possible criterion for selecting the NIR window is given by the FWHM of the inverse of these spectra as shown in Figure 7.
In addition to the total concentration of hemoglobin, the oxygen saturation will define the concentration of oxy- and deoxyhemoglobin in tissue and so the total absorption spectrum.
Below, the total concentration of hemoglobin is assumed to be 2.3 mM.
Then oxyhemoglobin will be dominant in the total absorption (black) and the effective attenuation (magenta) coefficient spectra, as shown in Figure 6 (a).
'cite: Anisotropic diffusion filter for dorsal hand vein features extraction – Sarah Hachemi Benziane, Abdelkader Benyettou' In this case
Then oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin will have similar contributions to the total absorption (black) and the effective attenuation (magenta) coefficient spectra, as shown in Figure 6 (b).
an arterial-venous blood volume ratio of 20%/80% can be adopted.
The total absorption (black) and the effective attenuation (magenta) coefficient spectra for breast tissue is shown in Figure 6 (c).
In addition, the effective penetration depth is plotted in Figure 7.