Parallel external memory
In computer science, a parallel external memory (PEM) model is a cache-aware, external-memory abstract machine.
[1] It is the parallel-computing analogy to the single-processor external memory (EM) model.
In a similar way, it is the cache-aware analogy to the parallel random-access machine (PRAM).
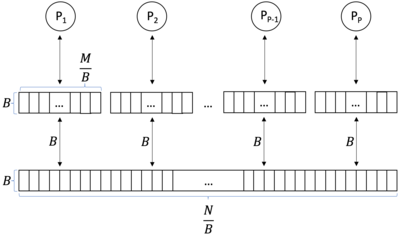
The PEM model consists of a number of processors, together with their respective private caches and a shared main memory.
processors and a two-level memory hierarchy.
small internal memories (caches).
The processors share the main memory.
A processor can't access another’s cache.
The processors can only perform operations on data which are in their cache.
The data can be transferred between the main memory and the cache in blocks of size
The complexity measure of the PEM model is the I/O complexity,[1] which determines the number of parallel blocks transfers between the main memory and the cache.
processors load parallelly a data block of size
form the main memory into their caches, it is considered as an I/O complexity of
A program in the PEM model should minimize the data transfer between main memory and caches and operate as much as possible on the data in the caches.
In the PEM model, there is no direct communication network between the P processors.
The processors have to communicate indirectly over the main memory.
If multiple processors try to access the same block in main memory concurrently read/write conflicts[1] occur.
Like in the PRAM model, three different variations of this problem are considered: The following two algorithms[1] solve the CREW and EREW problem if
The main idea is to schedule the write operations in a binary tree fashion and gradually combine the data into a single block.
This procedure is continued until all the data is combined in one block.
be a vector of d-1 pivots sorted in increasing order.
In the following algorithm[1] the input is partitioned into N/P-sized contiguous segments
The multiway partitioning algorithm (PEM_DIST_SORT[1]) uses a PEM prefix sum algorithm[1] to calculate the prefix sum with the optimal
pivots M and the input set A are located in contiguous memory, then the d-way partitioning problem can be solved in the PEM model with
The content of the final buckets have to be located in contiguous memory.
The selection problem is about finding the k-th smallest item in an unordered list A of size N. The following code[1] makes use of PRAMSORT which is a PRAM optimal sorting algorithm which runs in
Under the assumption that the input is stored in contiguous memory, PEMSELECT has an I/O complexity of: Distribution sort partitions an input list A of size N into d disjoint buckets of similar size.
the task is delegated to a cache-optimal single-processor sorting algorithm.
Otherwise the following algorithm[1] is used: The I/O complexity of PEMDISTSORT is: where If the number of processors is chosen that
is the time it takes to sort N items with P processors in the PEM model.