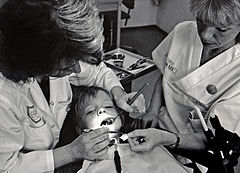
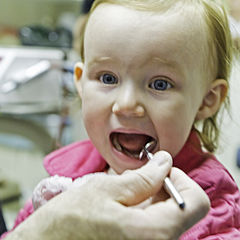
Pediatric dentistry
[4] Pediatric (also paediatric or pædiatric) dentists promote the dental health of children as well as serve as educational resources for parents.
Early detection is essential to maintain oral health, modify aberrant habits, and treat as needed and as simply as possible.
Additionally, parents are given a program of preventive home care (brushing, flossing and fluorides), a caries risk assessment, information on finger, thumb, and pacifier habits, and may include advice on preventing injuries to the mouth and teeth of children, diet counseling, and information on growth and development.
[7][8][9][10] The first dental care brought to public school was Alfred Fones in 1914, which was near 6 decades after the first woman, Lucy Hobbs Taylor, who received a DDS.
Third and fourth years of dental school focus on clinical care under the supervision of attending faculty who are licensed dentists.
In order to specialize in pediatric dentistry, one should receive additional in-depth training from an accredited postgraduate residency program.
At the end, resident dentists are awarded a certificate in pediatric dentistry with or without a master's degree depending on their program type.