Pensions in the United States
While various iterations of what could be considered pensions existed before the declared independence of the United States, most were designed solely for veterans of wars or set up as charitable initiatives by Church communities.
This trend continued throughout early American history, with much of the first veterans' pension under the newly formed United States offered to retired naval officers in 1799.
Eventually, responsibility for these pensions would be transferred to the Department of the Interior in 1849 as returning veterans from the Mexican–American War put further stress on the system.
[3] At the outset of the Civil War the General Law pension system was established by congress for both volunteer and conscripted soldiers fighting in the Union Army.
The compensation scheme later came to cover firefighters as well, growing into a lifetime pension plan about 20 years after its initial creation, with added funding from more substantial sources.
[10] The United States saw significant growth in pension plans, both public and private, throughout the Progressive Era as labor sought more rights from larger, and often more industrialized employers.
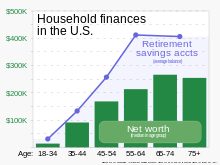
[12] The establishment of the Social Security system and numerous New Deal initiatives aimed at providing a safe net for elderly Americans caused an explosion in the size of the nation's federal retirement investment.
From the New Deal through the 1960s, numerous federal acts and regulations were created in order to encourage and protect the growing number of pensioners in the US.
Further shifts in tax regulations, age of participation, vesting status, and contribution limits would be set throughout the Reagan, Clinton, and Bush administrations.
[20] Non-Qualified plans are generally offered to employees at the higher echelons of companies as they do not qualify for income restrictions related to pensions.
[23] Multi-employer plans have courted a large degree of criticism in recent decades for corruption related to mob involvement and general misappropriation of pension funds.
[25] Nonetheless, Congress was compelled to establish further regulations and restrictions on the specific stripe of plan in 2014 with the Multiemployer Pension Reform Act of 2014 (MPRA).
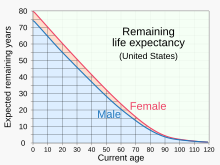
The amount of benefits is calculated based on the worker's average indexed monthly earnings (AIME) during their 35 highest-earning years.
Social Security also provides disability benefits for individuals unable to work due to physical or mental impairments.
As policymakers work to address the program's challenges, maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of Social Security is vital to safeguarding the well-being of current and future beneficiaries.