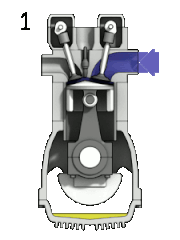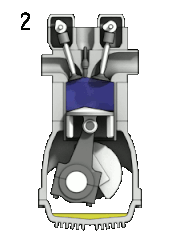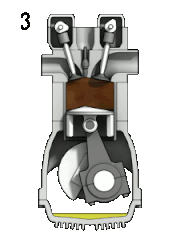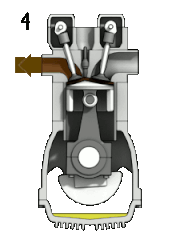
Petrol engine
Petrol engines can often be adapted to also run on fuels such as liquefied petroleum gas and ethanol blends (such as E10 and E85).
[1][2][3] The first practical petrol engine was built in 1876 in Germany by Nicolaus August Otto and Eugen Langen, although there had been earlier attempts by Étienne Lenoir in 1860, Siegfried Marcus in 1864 and George Brayton in 1873.
High voltage for the spark this may be provided by a magneto or an ignition coil.
Ignition modules can also function as a rev limiter in some cases to prevent overrevving and the consequences of it, such as valve float and connecting rod failure.
[13] Applications of petrol engines include automobiles, motorcycles, aircraft, motorboats and small engines (such as lawn mowers, chainsaws and portable generators).