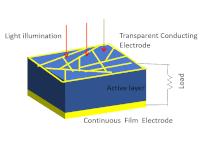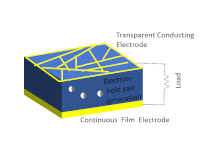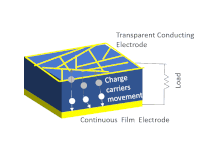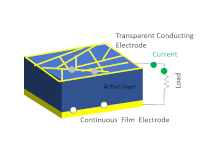
Photovoltaics
[9] In some instances, PV has offered the cheapest source of electrical power in regions with a high solar potential, with a bid for pricing as low as 0.015 US$/kWh in Qatar in 2023.
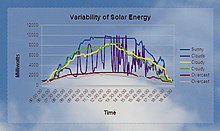
[21] The actual power output at a particular place may be less than or greater than this rated value, depending on geographical location, time of day, weather conditions, and other factors.
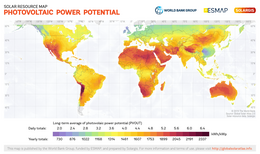
[24] The global regions that have high radiation levels throughout the year are the middle east, Northern Chile, Australia, China, and Southwestern USA.
This correlation between the power output of a solar cell and the working temperature of its junction depends on the semiconductor material, and is due to the influence of T on the concentration, lifetime, and mobility of the intrinsic carriers, i.e., electrons and gaps.
Advancements in photovoltaic technologies have brought about the process of "doping" the silicon substrate to lower the activation energy thereby making the panel more efficient in converting photons to retrievable electrons.
[45] Chemicals such as boron (p-type) are applied into the semiconductor crystal in order to create donor and acceptor energy levels substantially closer to the valence and conductor bands.
The degradation index, which is defined as the annual percentage of output power loss, is a key factor in determining the long-term production of a photovoltaic plant.
This is melted down when small amounts of boron, a group III element, are added to make a p-type semiconductor rich in electron holes.
The values of human labor and water consumption, for example, are not precisely assessed due to the lack of systematic and accurate analyses in the scientific literature.
[53][obsolete source] Life-cycle assessments, which look at all different environment effects ranging from global warming potential, pollution, water depletion and others, are unavailable for PV.
[54][better source needed] Thus, estimates of the environmental impact of PV have focused on carbon dioxide equivalents per kWh or energy pay-back time (EPBT).
[56] The EPBT has also been defined completely differently as "the time needed to compensate for the total renewable- and non-renewable primary energy required during the life cycle of a PV system" in another study, which also included installation costs.
In one such study, conventional energy mix in Greece was compared to multi-si PV and found a 95% overall reduction in effects including carcinogens, eco-toxicity, acidification, eutrophication, and eleven others.
[74] by Contrary to established thin films such as CIGS and CdTe, CZTS, Zn3P2, and SWCNT PVs are made from earth abundant, nontoxic materials and have the potential to produce more electricity annually than the current worldwide consumption.
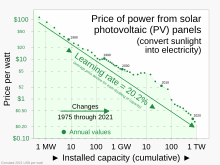
In late 2011, factory-gate prices for crystalline-silicon photovoltaic modules suddenly dropped below the $1.00/W mark, taking many in the industry by surprise, and has caused a number of solar manufacturing companies to go bankrupt throughout the world.
[87] Some environmentalists have promoted the idea that government incentives should be used in order to expand the PV manufacturing industry to reduce costs of PV-generated electricity much more rapidly to a level where it is able to compete with fossil fuels in a free market.
[102] For residential properties with private PV facilities networked to the grid, the owner may be able earn extra money when the time of generation is included, as electricity is worth more during the day than at night.
[103] One journalist theorised in 2012 that if the energy bills of Americans were forced upwards by imposing an extra tax of $50/ton on carbon dioxide emissions from coal-fired power, this could have allowed solar PV to appear more cost-competitive to consumers in most locations.
[109] Generous Feed-in tariff (FIT) and government supporting policies such as tax exemptions were the key to enable Vietnam's solar PV boom.
Crystalline silicon photovoltaics are only one type of PV, and while they represent the majority of solar cells produced currently there are many new and promising technologies that have the potential to be scaled up to meet future energy needs.
As of 2018, crystalline silicon cell technology serves as the basis for several PV module types, including monocrystalline, multicrystalline, mono PERC, and bifacial.
Reported global warming potential impacts of CIGS ranges 20.5–58.8 grams CO2-eq/kWh of electricity generated for different solar irradiation (1,700 to 2,200 kWh/m2/y) and power conversion efficiency (7.8 – 9.12%).
Some of the benefits for DSC is that it can be used in a variety of light levels (including cloudy conditions), it has a low production cost, and it does not degrade under sunlight, giving it a longer lifetime then other types of thin film solar cells.
Because organic photovoltaics require very high purity and are relatively reactive they must be encapsulated which vastly increases the cost of manufacturing and means that they are not feasible for large scale-up.
[141] TEGs rely on the Seebeck effect, a phenomenon that occurs when a junction of two conducting materials experience a temperature difference thereby, inducing an electromotive force.
In case the zenith distance of the Sun reaches zero, the "ladder" may be rotated to the north or the south to avoid a solar module producing a shadow on a lower one.
[148] Concentrator photovoltaics is a technology that contrary to conventional flat-plate PV systems uses lenses and curved mirrors to focus sunlight onto small, but highly efficient, multi-junction solar cells.
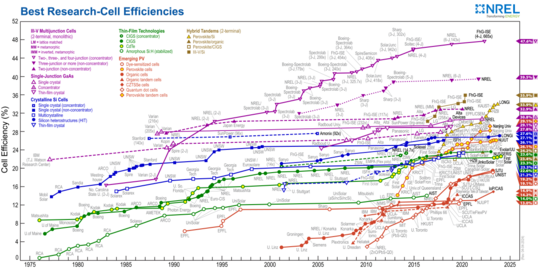
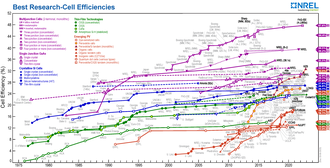
[149] The highest efficiencies achieved without concentration include a material by Sharp Corporation at 35.8% using a proprietary triple-junction manufacturing technology in 2009,[150] and Boeing Spectrolab (40.7% also using a triple-layer design).
For example, MIT estimated that 52,000 people per year die prematurely in the U.S. from coal-fired power plant pollution[159] and all but one of these deaths could be prevented from using PV to replace coal.
The city of Berkeley developed an innovative financing method to remove this limitation, by adding a tax assessment that is transferred with the home to pay for the solar panels.