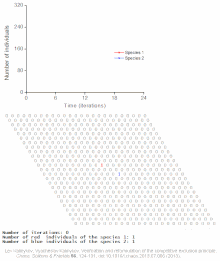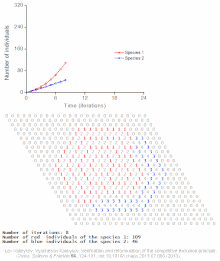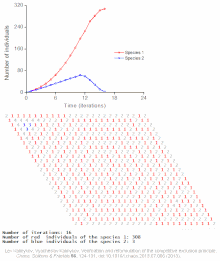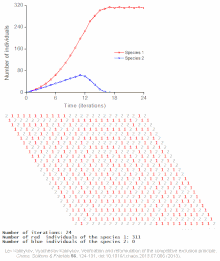
Population model
Modeling of dynamic interactions in nature can provide a manageable way of understanding how numbers change over time or in relation to each other.
[2] Population models are used to determine maximum harvest for agriculturists, to understand the dynamics of biological invasions, and for environmental conservation.
Thomas Malthus was one of the first to note that populations grew with a geometric pattern while contemplating the fate of humankind.
Lotka developed paired differential equations that showed the effect of a parasite on its prey.
Matrix algebra was used by Leslie in conjunction with life tables to extend the work of Lotka.