Post-war
The term "post-war" can have different meanings in different countries and refer to a period determined by local considerations based on the effect of the war there.
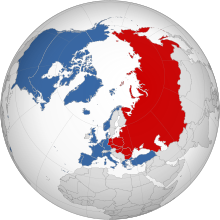
Some examples of post-war events are in chronological order: The Cold War was a geopolitical conflict between the capitalist and liberal "democratic" United States, the authoritarian and Communist Marxist–Leninist Soviet Union, and their respective allies: NATO and the Western Bloc for the United States, and the Warsaw Pact and the Eastern Bloc for the Soviet Union.
At the height of the cold war, both superpowers manufactured and deployed thousands of nuclear weapons to target each other's key economic, military, and political centers.
Each superpower's buildup and demonstration of nuclear strike capabilities lead to an unofficial military doctrine known as mutual assured destruction (MAD).
The Cold War began to come to an end in 1989 with the overthrow of Communist governments across Eastern Europe in the Revolutions of 1989 which was followed shortly after by the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, leaving the United States the world's sole superpower.