Prime number
[13] The Rhind Mathematical Papyrus, from around 1550 BC, has Egyptian fraction expansions of different forms for prime and composite numbers.
[14] However, the earliest surviving records of the study of prime numbers come from the ancient Greek mathematicians, who called them prōtos arithmòs (πρῶτος ἀριθμὸς).
[18] Another Islamic mathematician, Ibn al-Banna' al-Marrakushi, observed that the sieve of Eratosthenes can be sped up by considering only the prime divisors up to the square root of the upper limit.
His book Liber Abaci (1202) was the first to describe trial division for testing primality, again using divisors only up to the square root.
[22] Euler proved Alhazen's conjecture (now the Euclid–Euler theorem) that all even perfect numbers can be constructed from Mersenne primes.
[24] Ideas of Bernhard Riemann in his 1859 paper on the zeta-function sketched an outline for proving the conjecture of Legendre and Gauss.
[26] Many mathematicians have worked on primality tests for numbers larger than those where trial division is practicably applicable.
[33] The increased practical importance of computerized primality testing and factorization led to the development of improved methods capable of handling large numbers of unrestricted form.
[46] By the early 20th century, mathematicians began to agree that 1 should not be listed as prime, but rather in its own special category as a "unit".
[62] Weaker statements than this have been proven; for example, Vinogradov's theorem says that every sufficiently large odd integer can be written as a sum of three primes.
a result that is known to follow from the Riemann hypothesis, while the much stronger Cramér conjecture sets the largest gap size at
This area of study began with Leonhard Euler and his first major result, the solution to the Basel problem.
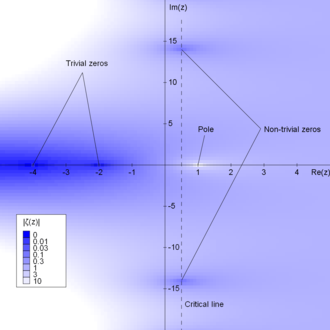
This function is closely connected to the prime numbers and to one of the most significant unsolved problems in mathematics, the Riemann hypothesis.
, is the limiting probability that two random numbers selected uniformly from a large range are relatively prime (have no factors in common).
Dirichlet's theorem on arithmetic progressions, in its basic form, asserts that linear polynomials with relatively prime integers
Stronger forms of the theorem state that the sum of the reciprocals of these prime values diverges, and that different linear polynomials with the same
[93] The Euler product can be derived from the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, and shows the close connection between the zeta function and the prime numbers.
[96] The original proof of the prime number theorem was based on a weak form of this hypothesis, that there are no zeros with real part equal to
The corresponding mapping to an additive group would be the logarithm of the absolute value, although this does not meet all the requirements of a valuation.
[121] In particular, number theorists such as British mathematician G. H. Hardy prided themselves on doing work that had absolutely no military significance.
is prime are probabilistic (or Monte Carlo) algorithms, meaning that they have a small random chance of producing an incorrect answer.
[131] When the elliptic curve method concludes that a number is prime, it provides primality certificate that can be verified quickly.
[154] As of December 2019[update] the largest number known to have been factored by a general-purpose algorithm is RSA-240, which has 240 decimal digits (795 bits) and is the product of two large primes.
As of October 2012[update], the largest number that has been factored by a quantum computer running Shor's algorithm is 21.
[166] Another example is Eisenstein's criterion, a test for whether a polynomial is irreducible based on divisibility of its coefficients by a prime number and its square.
[170] Beyond mathematics and computing, prime numbers have potential connections to quantum mechanics, and have been used metaphorically in the arts and literature.
[175] Beginning with the work of Hugh Montgomery and Freeman Dyson in the 1970s, mathematicians and physicists have speculated that the zeros of the Riemann zeta function are connected to the energy levels of quantum systems.
The French composer Olivier Messiaen used prime numbers to create ametrical music through "natural phenomena".
[184] In his science fiction novel Contact, scientist Carl Sagan suggested that prime factorization could be used as a means of establishing two-dimensional image planes in communications with aliens, an idea that he had first developed informally with American astronomer Frank Drake in 1975.
[185] In the novel The Curious Incident of the Dog in the Night-Time by Mark Haddon, the narrator arranges the sections of the story by consecutive prime numbers as a way to convey the mental state of its main character, a mathematically gifted teen with Asperger syndrome.