PulseAudio
The NT kernel was previously supported via MinGW (an implementation of the GNU toolchain, which includes various tools such as GCC and binutils).
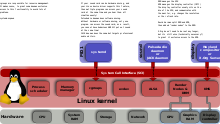
[11] One of the goals of PulseAudio is to reroute all sound streams through it, including those from processes that attempt to directly access the hardware (like legacy OSS applications).
In a typical installation scenario under Linux, the user configures ALSA to use a virtual device provided by PulseAudio.
There is support for PulseAudio in the GNOME project, and also in KDE, as it is integrated into Plasma Workspaces, adding support to Phonon (the KDE multimedia framework) and KMix (the integrated mixer application) as well as a "Speaker Setup" GUI to aid the configuration of multi-channel speakers.
Tizen, an open-source mobile operating system, which is a project of the Linux Foundation and is governed by a Technical Steering Group (TSG) composed of Intel and Samsung, uses PulseAudio.
[36] PipeWire is an audio and video server that "aims to support the use cases currently handled by both PulseAudio and Jack".