Pyrithione
Pyrithione is the common name of an organosulfur compound with molecular formula C5H5NOS, chosen as an abbreviation of pyridinethione, and found in the Persian shallot.
[1] It is used to prepare zinc pyrithione,[9][10] which is used primarily to treat dandruff and seborrhoeic dermatitis in medicated shampoos,[11][12] though is also an anti-fouling agent in paints.
Pyrithione is found as a natural product in the Allium stipitatum plant, an Asian species of onion, also known as the Persian shallot.
[21] However, as apoptosis only occurs in higher organisms, this mechanism isn't relevant to the antifungal and bacteric idal properties of pyrithione.
Pyrithione exists as a pair of prototropes, a form of tautomerism whereby the rapid interconversion of constitutional isomers involves the shift of a single proton, in this case between the sulfur and oxygen atoms (shown in the infobox above).
In the solid state, it forms a dimer in which each zinc centre adopts a trigonal bipyramidal geometry with two of the anions acting as bridging ligands coordinated through the oxygen atoms in the axial positions.
[31][32] It can be used as an antibacterial agent against Staphylococcus and Streptococcus infections for conditions such as athlete's foot, eczema, psoriasis, and ringworm.
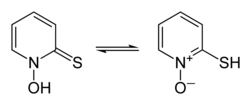


(thione form on the left, thiolate form on the right)