QF 3-inch 20 cwt
Beginning in 1930, a new towed 4-wheeled sprung trailer platform on pneumatic tyres was introduced to replace the obsolete lorries and two-wheeled carriages still used as mounts from World War I, barrels were equipped with loose liners, and the guns were connected to the new Vickers No.
When war broke out and Germany occupied Belgium and North-east France, it was realised that key installations in England could be attacked by air.
The Navy provided the initial 3-inch (76 mm) guns from its warships, approximately 18 by December 1914, for the defence of key installations in Britain, manned by RNVR crews, until the new specialised anti-aircraft version began production and entered service.
However, the Mobile Anti-Aircraft Brigade based at Kenwood Barracks in London, continued to be manned by the RNVR, although under the operational control of the Army.
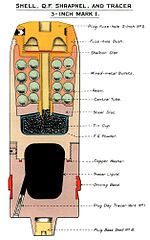
The 3-inch 20 cwt with its powerful and stable in flight,[18] 16 lb (7.3 kg) shell and fairly high altitude was well suited to defending the United Kingdom against high-altitude Zeppelins and bombers.
[9] This means that the gun team had to calculate where the target would be 9 to 18 seconds ahead, determine the deflection and set the correct fuze length, load, aim and fire accordingly.
Deflection was calculated mechanically and graphically using an optical height & rangefinder to provide data for the two piece Wilson-Dalby 'predictor', with the fuze length read off a scale mounted on the gun.
However, the powder burning rate changed as air pressure reduced, making them erratic for the new vertical shooting.
Over the 1930s, they had been gradually modernized, and a limited production line was set up at the Commonwealth Ordnance Factory Maribyrnong, Australia.
[28] One hundred and twenty were in France with the British Expeditionary Force in November 1939, compared with 48 of the modern QF 3.7-inch AA gun.
It was also fitted to older destroyers, A-class to I class during refits in 1940, replacing a set of torpedo tubes, to increase their AA capabilities.
[2] Britain supplied 24 Mk 3 guns and 7 M/34 mechanical fire control computers to Finland during the Winter War of 30 November 1939 to March 1940 but they arrived too late to be used.