RAB7A
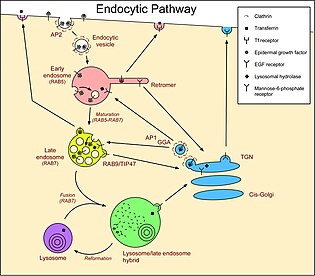
[8] Members of the RAB family of RAS-related GTP-binding proteins are important regulators of vesicular transport and are located in specific intracellular compartments.
[11] It is linked that RAB7a levels and function were independent of melanocyte lineage-specific transcription factors (MITF) but recent research has shown that SOX10 (a neuroectodermal master modulator) and MYC (an oncogene) are the major regulators.
Studies show that RAB7a can be specifically up regulated through MITF-independent manners like changing levels of SOX10 or MYC to affect tumor proliferation especially in melanoma[14].
RILP plays the role of a downstream effector for Rab7 and together both of these proteins act to regulate late endocytic traffic.
[7] Melanoma cells retain a developmental memory that reflects a unique wiring of vesicles trafficking pathways.
Rab7 is seen to control the proliferative and invasive potential of these aggressive tumors upon identification of melanoma enriched endolysosomal gene cluster.
It is speculated that downregulation of RAB7 in the invasive front of aggressive melanomas is modulated by epithelial-to-mesenchymal-like mechanisms, such as those recently described to underlie the transcriptional switch associated with prometastatic phenotypes.
In otherwords, there is an inherent dependency of melanoma cells on the small GTPase RAB7, identified within a lysosomal gene cluster that distinguishes this malignancy from over 35 tumor types.
Analyses in human cells, clinical specimens, and mouse models demonstrated that RAB7 is an early-induced melanoma driver whose levels can be tuned to favor tumor invasion, ultimately defining metastatic risk.
Importantly, RAB7 levels and function were independent of MITF and instead, the neuroectodermal master modulator SOX10 and the oncogene MYC are key RAB7a regulators.
This is a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of inherited disorders, characterized by prominent sensory loss, often complicated by severe ulcero-mutilations of toes or feet, and variable motor involvement.