Radiation exposure
[4] We know this from the Life Span Study, which followed survivors of the atomic bombing in Japan during World War 2.
[8] Complications from radiation exposure include malformation of internal organs, reduction of IQ, and cancer formation.
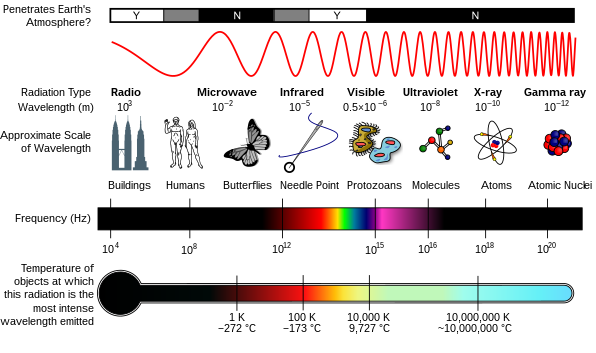
[4] Electromagnetic radiation consists of photons, which can be thought of as energy packets, traveling in the form of a wave.
[7] One reason why is that a long period of time occurs from exposure to radiation and the appearance of cancer.
[7] It is difficult to determine whether increases in cancer in a population are caused by low dose radiation.
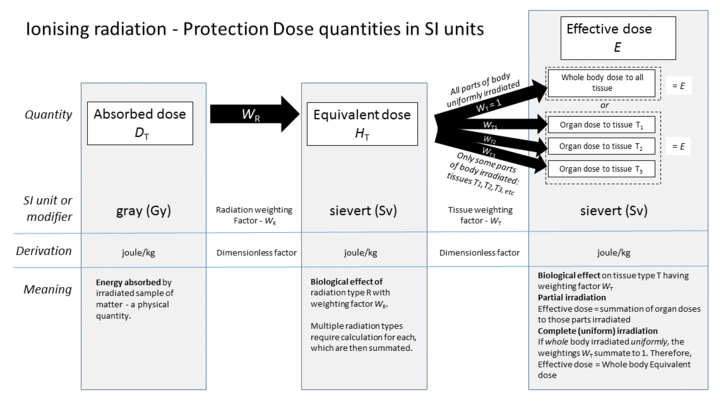
[4] Another common measurement for human tissue is Gray (Gy, International or SI unit).
[4] The dose equivalent measures the effective radiation dosage in a specific organ or tissue.
[4] For example, suppose a person's small intestine and stomach are both exposed to radiation separately.
The tissue weighting factors of various organs are listed in the following table:[2] Adrenals, Extrathoracic (ET) region, Gall bladder, Heart, Kidneys, Lymphatic nodes, Muscle, Oral mucosa, Pancreas, Prostate, Small intestine, Spleen, Thymus, Uterus/cervix.
[7] The population was defined as those selected to include three major groups of registered Hiroshima and Nagasaki residents: (1) atomic bomb survivors who were within 2.5 km of the hypocenter at the time of the bombings (ATB), (2) survivors who were between 2.5 and 10 km of the hypocenter ATB (low- or no-dose group), and (3) residents who were temporarily not in either Hiroshima or Nagasaki or were more than 10 km from the hypocenter in either city (NIC) at the time of the bombings (no-exposure group).
[7] The International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) describes how deterministic effects, or harmful tissue reactions, occur.
[5] It is possible to assume that the incidence of cancer will rise with the equivalent dose in the relevant organs and tissues.
[5] Doses below this threshold of 100 mSv will produce a direct increase in probability of incurring cancer.
Because of this uncertainty at low doses, the Commission does not calculate the hypothetical number of cancer cases.
[5] In the healthcare field, professionals can be exposed to various forms of ionization if they do not take the appropriate preventive measures.
The implementation of preventive measures is essential in order to decrease the risk of exposure and to make sure healthcare workers are safe and protected.
These trainings also cover the use of personal protective equipment, ensuring personnel wear proper aprons/scrubs, shields/masks, goggles, gloves, etc.
[14] When patients were provided an antioxidant treatment before radiation exposure, DNA damage measured as double-strand breaks in peripheral blood lymphocytes was decreased.
[15] Also in rats, antioxidant treatment ameliorated germ cell apoptosis induced by high-dose ionizing irradiation.
[5] Radon gas is a radioactive chemical element that is the largest source of background radiation, about 2mSv per year.
[18] Aside from medical imaging, other man-made sources of radiation include building and road construction materials[19], combustible fuels, including gas and coal, televisions, smoke detectors, luminous watches, tobacco, some ceramics, and more in the reference.
Below is an example from the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission on how different types of food contain small amounts of radiation.
[23] The sources of radiation are radioactive potassium-40 (40K), radium-226 (226Ra), and other atoms:[23] For decades, standard man was used as a reference, ignoring female and developing organisms.
[8] This is the phase of development where the three germ layers (the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) form the internal organs of the fetus.
[24] The estimated dose threshold is 0.1 Gylow-linear-energy-transfer (LET) radiation, and this period generally occurs from day 14–50.
In addition, the United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation calculated excess relative risk in the first trimester.
[26] Screening imaging exams are used to catch cancer early, reducing the risk of death.
[28] Aside from cancer, many types of medical imaging are used to diagnose life-threatening diseases, such as heart attacks, pulmonary embolism, and pneumonia.
[29][30][31] The gamma ray field can be characterized by the exposure rate (in units of, for instance, roentgen per hour).
They give the exposure rate in roentgens per hour for a given activity in millicuries at a distance in centimeters.