Regions of the African Union
The member states of the African Union (AU) are divided into five geographical regions.
[1] When a principal organ of the United Nations allocates a certain number of seats to the African Group, such as on the UN Security Council or the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC), the African Union distributes these seats based on these geographical regions[2] (however, even though Morocco was not a member of the African Union between 1984-2017, it was still eligible to be picked).
States must apply to the Executive Council's Committee on Candidatures by March of the election year in order to become a candidate.
[8] More specifically, the African Union Handbook (2021) states: In January 2008, the Executive Council suggested that the African diaspora be treated as Africa’s sixth region and its participation in the AU’s organs and activities be strengthened (EX.CL/Dec.406(XII)).
[9] Additionally, the African Union works together with AfricaRecruit, the Caribbean Community and Common Market, the Commonwealth Business Council, the International Organization for Migration, and the World Bank to facilitate African diaspora relations, regionally and internationally.
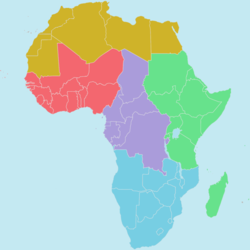
Central
Eastern
Northern
Southern
Western
Note that Ceuta and Melilla in Northern Africa are parts of Spain .