IT risk management
The continuous update and maintenance of an ISMS is in turn part of an organisation's systematic approach for identifying, assessing, and managing information security risks.
"[5] The American National Information Assurance Training and Education Center defines risk management in the IT field as:[6]
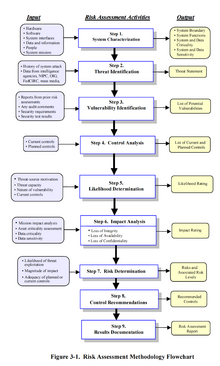
This step involves gathering relevant information about the organization and defining the criteria, scope, and boundaries of the risk management activities.
This includes complying with legal requirements, ensuring due diligence, and supporting the establishment of an information security management system (ISMS).
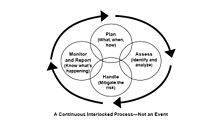
It forms the foundation for ongoing risk management, which includes analysis, planning, implementation, control, and monitoring of security measures.
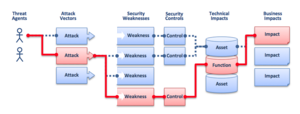
The result of this step is a list of risks, threats, and potential consequences related to the assets and business processes.
The following strategies are typically considered:[5] Residual risks, those remaining after treatment, are estimated to ensure adequate protection, and further measures may be taken if necessary.
Risk management is an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and review to ensure that implemented security measures remain effective as business conditions, threats, and vulnerabilities change.
Each phase of the SDLC benefits from specific risk management activities, from initial planning to system disposal.
Risk management as a methodology has been criticized for its subjectivity, particularly in assessing the value of assets and the likelihood and impact of threats.