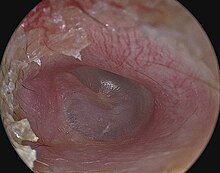
Perforated eardrum
Other symptoms may include tinnitus, ear pain, vertigo, or a discharge of mucus.
[3] This may take the form of a paper patch to promote healing (a simple procedure by an ear, nose and throat specialist), or surgery (tympanoplasty).
The objective of the surgery is to provide a platform of sort to support the regrowth and healing of the tympanic membrane in the two weeks post-surgery period.
Predictors of failure includes young age and poor Eustachian tube function.
[9] The use of minimally invasive endoscopic technique does not reduce the chance of successful outcome.