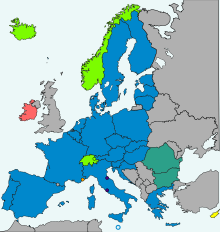
Schengen Agreement
[1] In 1990, the Agreement was supplemented by the Schengen Convention which proposed the complete abolition of systematic internal border controls and a common visa policy.
[1] In 1990, the Agreement was supplemented by the Schengen Convention which proposed the abolition of internal border controls and a common visa policy.
but just over two years later during the Amsterdam Intergovernmental Conference, all European Union member states except the United Kingdom and Ireland had signed the Agreement.
[13] Legal acts setting out the conditions for entry into the Schengen Area are now made by majority vote in the EU's legislative bodies.
[14] In 2016, border controls were temporarily reintroduced in seven Schengen countries (Austria, Denmark, France, Germany, Norway, Poland, and Sweden) in response to the European migrant crisis.
[18] On 8 December 2022, the Justice and Home Affairs Council voted to admit Croatia to the Schengen Area, effective from 1 January 2023.
[19] On 30 December 2023, the Justice and Home Affairs Council agreed to partially include Bulgaria and Romania in the Schengen Area, with air and maritime border checks lifted from 31 March 2024.
[20] On 12 December 2024, the Council decided to lift the remaining border checks at land crossing effective 1 January 2025, making Bulgaria and Romania full members of the Schengen Area.