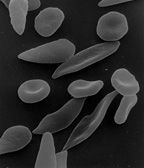
Sickle cell disease
[1] A number of health problems may develop, such as attacks of pain (known as a sickle cell crisis) in joints, anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections, dizziness[8] and stroke.
The liver, heart, kidneys, gallbladder, eyes, bones, and joints can be damaged from the abnormal functions of the sickle cells and their inability to effectively flow through the small blood vessels.
[4] The care of people with sickle cell disease may include infection prevention with vaccination and antibiotics, high fluid intake, folic acid supplementation, and pain medication.
[21] When SCD presents within the first year of life, the most common problem is an episode of pain and swelling in the child's hands and feet, known as dactylitis or "hand-foot syndrome."
Symptoms include pain on the left side, swollen spleen (which can be detected by palpation), fatigue, dizziness, irritability, rapid heartbeat, or pale skin.
[31][32] Aplastic crises are instances of an acute worsening of the patient's baseline anaemia, producing pale appearance, fast heart rate, and fatigue.
[35] Sickle cell anaemia can lead to various complications including:[36] Hemoglobin is an oxygen-binding protein, found in erythrocytes, which transports oxygen from the lungs (or in the fetus, from the placenta) to the tissues.
Under conditions of low oxygen concentration in the bloodstream, such as exercise, stress, altitude or dehydration, HbS polymerization forms fibrous precipitates within the red blood cell.
[62] In people heterozygous for HbS (carriers of sickle cell disease), the polymerisation problems are minor because the normal allele can produce half of the haemoglobin.
[69] Due to the adaptive advantage of the heterozygote, the disease is still prevalent, especially among people with recent ancestry in malaria-stricken areas, such as Africa, the Mediterranean, India, and the Middle East.
If sickling takes place in the venous system, after blood has passed through the capillaries, it has no effect on the organs and the RBCs can unsickle when they become oxygenated in the lungs.
[77][75] The rapid breakdown of RBC's in SCD results in the release of free heme into the bloodstream exceeding the capacity of the body's protective mechanisms.
Free heme is also an alarmin - a signal of tissue damage or infection, which triggers defensive responses in the body and increases the risk of inflammation and vaso-occlusive events.
[78][79] Checking for SCD begins during pregnancy, with a prenatal screening questionnaire which includes, among other things, a consideration of health issues in the child's parents and close relatives.
[80] A routine heel prick test, in which a small sample of blood is collected a few days after birth, is used to check conclusively for SCD as well as other inherited conditions.
[95][96] Hydroxyurea was the first approved drug for the treatment of SCD, which has been shown to decrease the number and severity of attacks and possibly increase survival time.
[121] When treating avascular necrosis of the bone in people with sickle cell disease, the aim of treatment is to reduce or stop the pain and maintain joint mobility.
[157] Since 2000, neonatal screening of SCD has been performed at the national level for all newborns defined as being "at-risk" for SCD based on ethnic origin (defined as those born to parents originating from sub-Saharan Africa, North Africa, the Mediterranean area (South Italy, Greece, and Turkey), the Arabic peninsula, the French overseas islands, and the Indian subcontinent).
[160] Due to many adults in high-risk groups not knowing if they are carriers, pregnant women and both partners in a couple are offered screening so they can get counselling if they have the sickle cell trait.
[164] In 2005, Saudi Arabia introduced a mandatory premarital test including HB electrophoresis, which aimed to decrease the incidence of SCD and thalassemia.
[167] Sickle cell disease is common in some ethnic groups of central India,[168] where the prevalence has ranged from 9.4 to 22.2% in endemic areas of Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Chhattisgarh.
[171] The first modern report of sickle cell disease may have been in 1846, where the autopsy of an executed runaway slave was discussed; the key finding was the absence of the spleen.
[173] The abnormal characteristics of the red blood cells, which later lent their name to the condition, was first described by Ernest E. Irons (1877–1959), intern to Chicago cardiologist and professor of medicine James B. Herrick (1861–1954), in 1910.
Irons saw "peculiar elongated and sickle-shaped" cells in the blood of a man named Walter Clement Noel, a 20-year-old first-year dental student from Grenada.
[18][174] Noel was readmitted several times over the next three years for "muscular rheumatism" and "bilious attacks" but completed his studies and returned to the capital of Grenada (St. George's) to practice dentistry.
Bill Cosby's Emmy-winning 1972 TV movie, To All My Friends on Shore, depicted the story of the parents of a child with sickle cell disease.
It often leads the excluded individual to experience emotional distress and may result in their academic underperformance, avoidance of school, and occupational failure later in life.
[190] The reliance on theories related to environmental factors to place blame on the mother reflects many Ugandan's poor knowledge of how the disease is acquired as it is determined by genetics, not environment.
[190] This lack of access to resources results from their subordinating roles within familial structures as well as the class disparities that hinder many mothers' ability to satisfy additional childcare costs and responsibilities.
The second aim was to set up a new training programme to help paramedics, Accident and Emergency staff, carers and the general public to care effectively for sufferers in crisis.